How to Deal with Stress When Caring for Dementia Patients
Caring for somebody with dementia can quickly begin to take over your life. But as much as you love your...
USPSTF: Screening Can Help Identify Anxiety and Depression in Older Children and Teens
How a Slipped Disc Impacts Your Health
 Tooth discoloration is such a common issue. It can be caused by improper brushing habits, smoking, or even drinking too many dark beverages like coffee or tea. So, people often opt for teeth whitening as a resolution.
Teeth whitening isn’t the only solution for tooth discoloration. Dental veneers, which are little shells that get placed over the teeth, can cover up yellowed teeth or teeth with brown spots quite effortlessly. This way, you won’t have to worry about regularly getting your teeth bleached or purchasing expensive teeth-whitening products.
Tooth discoloration is such a common issue. It can be caused by improper brushing habits, smoking, or even drinking too many dark beverages like coffee or tea. So, people often opt for teeth whitening as a resolution.
Teeth whitening isn’t the only solution for tooth discoloration. Dental veneers, which are little shells that get placed over the teeth, can cover up yellowed teeth or teeth with brown spots quite effortlessly. This way, you won’t have to worry about regularly getting your teeth bleached or purchasing expensive teeth-whitening products.
Brain Waves Form Unique “Fingerprint” For Each Person
What is compassion fatigue?
 Compassion fatigue is when you are exposed to suffering, trauma, or similar negative emotional states in others so much that you become desensitized and indifferent to it. You may also hear it referred to as secondary trauma or vicarious trauma, with many arguing that it’s an inevitable response.
Whichever name you use, it’s a condition in which you feel physically and psychologically exhausted, resulting in a diminished capacity for empathy. This, in turn, has a negative impact on your ability to do your job as a nurse.
Sadly, compassion fatigue is not uncommon in the healthcare field, which is why it’s so important to be alert to the symptoms and understand how to respond when they arise.
(more…)
Compassion fatigue is when you are exposed to suffering, trauma, or similar negative emotional states in others so much that you become desensitized and indifferent to it. You may also hear it referred to as secondary trauma or vicarious trauma, with many arguing that it’s an inevitable response.
Whichever name you use, it’s a condition in which you feel physically and psychologically exhausted, resulting in a diminished capacity for empathy. This, in turn, has a negative impact on your ability to do your job as a nurse.
Sadly, compassion fatigue is not uncommon in the healthcare field, which is why it’s so important to be alert to the symptoms and understand how to respond when they arise.
(more…)Inflammation Leads to Epigenetic and Metabolic Changes that Benefit Cancer.
Hair Straightening Chemicals May Increase Uterine Cancer Risk
UCLA Study Finds Kids Attending Higher Performing Charter Schools Had Lower Alcohol and Marijuana Use
Study Finds Reduced Kidney Disease Progression with DOACs vs Vitamin K Antagonists
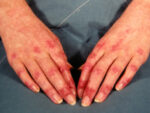
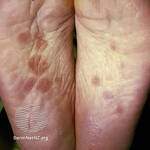
NEJM: Trial of IVIG for Autoimmune Disorder Dermatomyositis
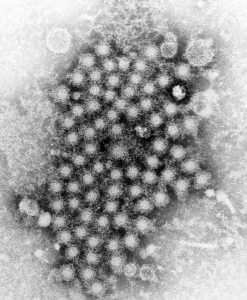
Hepatitis C: Few Insured Persons Receive Timely Treatment, and Disparities Exist
Most Common Health Concerns in the Elderly
USPSTF Recommends Syphilis Screening for Those at Risk
Non-Clinical Medical Careers are Soaring: Here is What You Need to Know
Healthcare is one of the largest industries in the country, and it is also outpacing other industries in terms of...
Myths About Teenager Sleep Needs Are Common
3 Things You Should Know When Caring for Your Elderly Relatives
It is incredibly important that you learn how to communicate and understand the loved ones that you are looking to...
Covid: Safety Net Hospitals Experienced Greater Financial Losses During Pandemic
Allison Witman PhD Assistant Professor of Economics Economics & Finance Cameron School of Business University of North Carolina, Wilmington
Yu Wang PhD Assistant Professor Congdon School of Supply Chain, Business Analytics, & Information Systems Cameron School of Business University of North Carolina Wilmington David Cho PhD Assistant Professor of Management California State University, Fullerton
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: The COVID-19 pandemic placed tremendous financial pressure on hospitals. Beginning in March of 2020, hospitals cancelled outpatient and elective procedures to accommodate surges in demand from COVID-19 patients. As these procedures account for more than 60% of an average hospital’s revenue, cancellation posed serious challenges to the financial health of hospitals. Revenue from COVID-19 patients may have partially offset these effects, but the American Hospital Association estimated a total loss of $202.6 billion by American hospitals between March and June 2020. In response, the U.S. government created large federal assistance programs aimed to stabilize hospitals’ financial situation as their ability to maintain operations was critical to the health of the nation. Due to differences in hospital characteristics, certain hospitals such as rural hospitals and those serving a higher share of Medicaid and uninsured patients (e.g., safety net hospitals) may have been more financially susceptible to the effects of the pandemic. These hospitals that serve vulnerable patient populations historically have had lower profit margins and were candidates for targeted COVID relief funding (e.g., Safety Net Hospitals Payments, a $10 billion component of the Provider Relief Fund). (more…)Night Owls May Have Increased Risk of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease
Frailty Scores in Elderly Unaffected by Supplemental Omega-3 or Vitamin D
Hospital-Treated Infections And Risk of Later Life Neurodegenerative Diseases
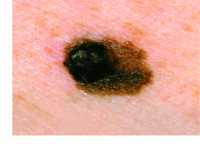
Melanoma: Tel-Aviv University Study Finds Blocking Two Key Proteins May Block Brain Metastases
USPSTF: Assesses Benefits and Harms of Screening for Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents
BIOGEN: Trial of Anti-BDCA2 Antibody Litifilimab for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Harvard Study Evaluates Vitamin D and Omega-3 Supplementation on Frailty Prevention
Does Pollen Cause Your Asthma Here’s How To Handle It
Knowing about pollen forecasts might help you understand how much pollen will be released in your area and when....