Scientists Develop Mouse Embryo from Stem Cells, Including Brain and Beating Heart
COPD: Inhalers Don’t Always Work for Smokers
What is Meth Mouth?
- Severe tooth decay
- Tooth loss
- Missing teeth
- Broken teeth
- Cracked teeth
- Yellow or brown stains on teeth
- Gum disease
- Dry mouth
- Bad breath
- Meth sores
Tea Drinkers May Live Longer
Fewer New Medicines Available in Germany, Compared to United States
NEJM: Study Compares PCI to Medical Therapy to Reduce Death or Hospitalization from Heart Failure
Study Evaluates Sexual Health After Caesarean Vs Vaginal Delivery
Multiple Sclerosis: Decrease in Relapses and Brain Lesions with Ublituximab, Targeting B Cells
Study Examines Ways to Reduce Demand for Colonoscopies
Risk of Hip Fractures Greater in Vegetarians
Gestational Diabetes: Lower vs Higher Glucose Levels for Diagnosis
NEJM Study Suggests If Having Kidney Stone Surgery, Treat All the Stones
Increased Adrenal Hormone Aldosterone Linked to Greater Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease
Lifestyle Exposures Do Not Explain Why Men Are More Prone to Cancer
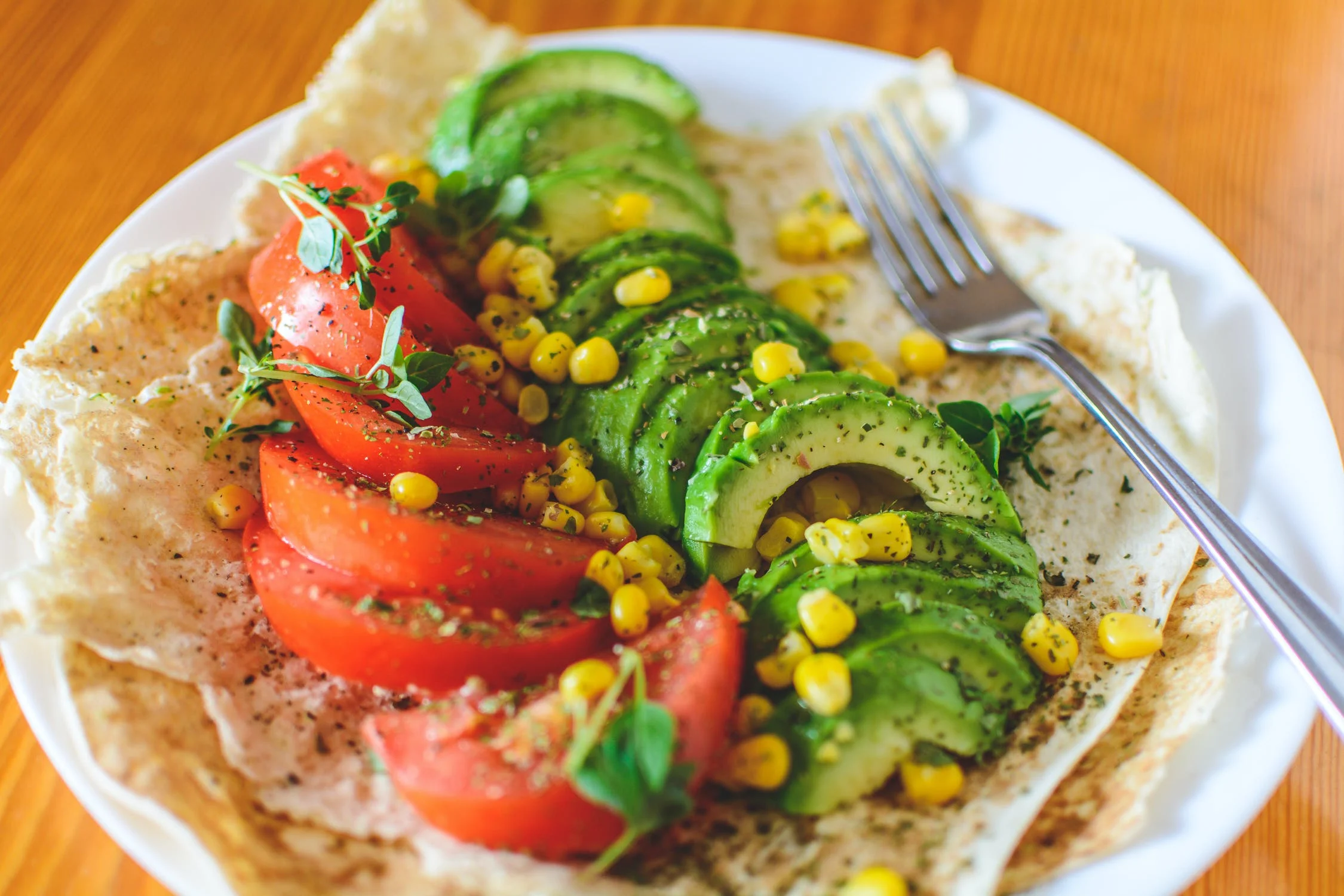
USPSTF: Evaluates Benefits of Diet and Exercise Counseling for Adults Without Known Heart Disease Risk Factors
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lori Pbert, Ph.D Professor, Department of Population and Quantitative Health Sciences Associate chief of the Division of Preventive and Behavioral Medicine Founder and director of the Center for Tobacco Treatment Research and Training University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School Dr. Pbert joined the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in January 2019
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Heart attacks and strokes are the number one killer of adults in the United States. Based on the evidence we reviewed, the Task Force found that some people would benefit from counseling interventions to support their cardiovascular health, however the overall benefits are small. For that reason, we continue to recommend that healthcare professionals decide together with their patients who do not have cardiovascular disease risk factors whether counseling interventions on healthy diet and physical activity might help them prevent heart attacks and strokes. This is a C grade recommendation. (more…)
Study Finds Promising Effects of Jarlsberg® Cheese on Bone and Metabolic Markers
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Stig Larsen PhD Professor Emeritus Controlled Clinical Research Methodology and Statistics Norwegian University of Life Sciences Oslo, Norway
MedicalResearch.com:? What are the main findings?
Response: Osteoporosis is a major problem among elderly and malnourished people. Calcium, Vitamin D and Vitamin K are beneficial for bone health. Vitamin D stimulates calcium absorption and studies have shown that poor Vitamin K status intake is linked to low bone mass. Osteocalcin (OC) is a protein hormone found in the blood in activated and inactivated form. The activated form of Osteocalcin (cOC) binds calcium to bone tissue and plays an important role in regulating the metabolism. In addition, low levels of cOC are associated with insulin resistance, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. It is desirable to have largest possible uOC, and vitamin K2 central in this process. The most important vitamin K2 variants in Jarlsberg® are the long-chain MK-7, -8, -9 and -9(4H), where lactic acid bacteria produce the first three, while MK-9(4H) is produced by Propionibacterium freudenreichii. The latter bacterium also produces the substance "1,4-dihydroxy-2- naphthoic acid" (DHNA), which has previously been shown to increase bone density in experimental mice. Two previous studies related to Jarlsberg® intake have been published:
- The first study showed that cOC in the blood increased with increasing Jarlsberg® dose up to a daily intake of 57 grams of Jarlsberg®. Even more startling was that the total OC (tOC) level increased significantly, and that triglycerides and cholesterol were significantly reduced.1
- The second study reproduced the findings from the first study and demonstrated additionally that the Jarlsberg dose of 57g/day could be reduced to 45 grams after 6 weeks without reducing the achieved level of tOC and vitamin K2.2
The BMJ-study3: The central variables measured in this study were the serum bone turnover markers (BTM); tOC and cOC, procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (PINP) and serum cross-linked C- telopeptide type I collagen (CTX). Additionally, Vitamin K2 and Vitamin K status, serum calcium and serum magnesium were recorded together with the development in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lipids and protein turnover. The participants in the study were randomly divided into two groups. One group of 41 healthy volunteer women of childbearing age ate 57 grams of Jarlsberg® per day and the other group of 25 women ate 50 grams of Camembert for 6 weeks. The Camembert was manufactured with a starting culture not producing Vitamin K2. The fat, protein, and energy content of the daily consumption of Jarlsberg® and Camembert is approximately the same. After 6 weeks, Camembert was replaced with 57 grams of Jarlsberg® per day for another 6 weeks. (more…)
Premature Menopause May Increase Risk of Heart Failure and AFib
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Jean Shin Department of Family Medicine Korea University College of Medicine Seoul,Republic of Korea
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Younger age at menopause is a possible risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. However, data on the association among premature menopause, age at menopause, and the risk of heart failure and atrial fibrillation are lacking. We aimed to examine the association of premature menopause and age at menopause with the risk of heart failure and atrial fibrillation. (more…)