MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Tara M Lovestead, PhD, (She/her/hers)
Group Leader | Fluid Characterization Group
Applied Chemicals and Materials Division
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Gaithersburg, MD
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: In 2012, when cannabis was decriminalized for adult recreational and medical use in Colorado, I started thinking about how a cannabis breathalyzer could work. I knew that an alcohol breathalyzer model would be pursued for a field sobriety test, but also knew that THC, the main psychoactive compound in cannabis, was a completely different animal, chemically speaking, than ethanol, the intoxicant in alcohol. I began by measuring the vapor pressure of THC and determined that it is a million times less volatile than ethanol. This is why the main strategy for measuring THC in breath is based on collecting breath aerosols with filters (ethanol is measured as a vapor in breath and does not need to be “collected”). My colleague, Dr. Kavita Jeerage and I began working together to design a study using a simple device that samples breath aerosols that hadn’t been used before. We designed this as a small study to piggyback on a larger study with our collaborator Prof. Cinnamon Bidwell at the University of Colorado, Boulder. Bidwell’s experience studying the effects of legal market cannabis product use on psychology and behavior was leveraged to launch the pilot study.
(more…)
Alzheimer's - Dementia, Author Interviews, Biomarkers, JAMA, MRI / 22.05.2023
Alzheimer’s Disease: Study Finds tau-PET Imaging Increases Diagnostic Accuracy
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Ruben Smith MD, PhD
Associate professor at Clinical Memory Research
Division of Neurology
Lund University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Since a few years it has become possible to visualize tau pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) using positron emission tomography (PET). The tau-PET radiotracer Flortaucipir (Tauvid) was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration as an AD diagnostic tool. Since PET imaging is costly and exposes the patient to radioactivity we wanted to study the added clinical value of tau-PET in the diagnostic work-up of patients with cognitive symptoms, before widespread implementation in clinical practice.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Heart Disease, JACC, Surgical Research / 22.05.2023
Novel Coating on Investigational WATCHMAN FLX™ Pro device May Reduce Risk of Embolism
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Aloke V. Finn MD
Medical Director/Chief Scientific Officer
CVPath Institute Inc.
Gaithersburg, MD 20878
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response:Transcatheter left atrial appendageal closure (LAAC) has become an established therapeutic approach for prevention of stroke in subjects with non-valvular atrial fibrillation who are ineligible for long-term oral anticoagulation. Device-related thrombus (DRT), developing after LAAO procedures occurs in a small proportion but patients receiving these devices but is associated with critical embolic events such as ischemic stroke. Thrombogenicity and delayed endothelialization of fabric play a role in the development of DRT. Fluorinated polymers are known to have thromboresistant properties which may favorably modify blood biomaterial interactions of a LAAO device.
In this study we compared the thrombogenicity and endothelial coverage (EC) after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) between a novel fluoropolymer-coated Watchman (FP-WM (Watchman FLX PRO) and the conventional uncoated Watchman FLX (WM).
(more…)
Alzheimer's - Dementia, Author Interviews, Cost of Health Care, JAMA, UCLA / 20.05.2023
New Alzheimer Drug Lecanemab and its Ancillary Services Could Cost Medicare up to 5 billion Annually
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Julia Cave Arbanas
Project Manager and
 John N. Mafi, MD, MPH
Associate Professor of Medicine
General Internal Medicine & Health Services Research
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What is lecanemab used for and how well does it work?
Response: Lecanemab is a treatment for mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia that was approved in January 2023 as part of the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) accelerated approval program. The results from a recent phase 3 clinical trial show a modest clinical benefit: the rate of cognitive decline by 27% in an 18-month study involving participants experiencing the early stage of Alzheimer’s, with an 0.45-point absolute difference in cognitive testing scores. However, due to the risk of brain swelling and bleeding (also known as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities), treatment with lecanemab involves frequent MRIs and neurology or geriatrics appointments to monitor for these abnormalities, which can be life threatening. So far, three patient deaths have potentially been tied to lecanemab.
It is likely that the FDA will grant is lecanemab traditional approval later this year, prompting Medicare to reconsider its current coverage restrictions and potentially enabling widespread use.
(more…)
John N. Mafi, MD, MPH
Associate Professor of Medicine
General Internal Medicine & Health Services Research
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What is lecanemab used for and how well does it work?
Response: Lecanemab is a treatment for mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia that was approved in January 2023 as part of the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) accelerated approval program. The results from a recent phase 3 clinical trial show a modest clinical benefit: the rate of cognitive decline by 27% in an 18-month study involving participants experiencing the early stage of Alzheimer’s, with an 0.45-point absolute difference in cognitive testing scores. However, due to the risk of brain swelling and bleeding (also known as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities), treatment with lecanemab involves frequent MRIs and neurology or geriatrics appointments to monitor for these abnormalities, which can be life threatening. So far, three patient deaths have potentially been tied to lecanemab.
It is likely that the FDA will grant is lecanemab traditional approval later this year, prompting Medicare to reconsider its current coverage restrictions and potentially enabling widespread use.
(more…)
 John N. Mafi, MD, MPH
Associate Professor of Medicine
General Internal Medicine & Health Services Research
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What is lecanemab used for and how well does it work?
Response: Lecanemab is a treatment for mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia that was approved in January 2023 as part of the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) accelerated approval program. The results from a recent phase 3 clinical trial show a modest clinical benefit: the rate of cognitive decline by 27% in an 18-month study involving participants experiencing the early stage of Alzheimer’s, with an 0.45-point absolute difference in cognitive testing scores. However, due to the risk of brain swelling and bleeding (also known as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities), treatment with lecanemab involves frequent MRIs and neurology or geriatrics appointments to monitor for these abnormalities, which can be life threatening. So far, three patient deaths have potentially been tied to lecanemab.
It is likely that the FDA will grant is lecanemab traditional approval later this year, prompting Medicare to reconsider its current coverage restrictions and potentially enabling widespread use.
(more…)
John N. Mafi, MD, MPH
Associate Professor of Medicine
General Internal Medicine & Health Services Research
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What is lecanemab used for and how well does it work?
Response: Lecanemab is a treatment for mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia that was approved in January 2023 as part of the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) accelerated approval program. The results from a recent phase 3 clinical trial show a modest clinical benefit: the rate of cognitive decline by 27% in an 18-month study involving participants experiencing the early stage of Alzheimer’s, with an 0.45-point absolute difference in cognitive testing scores. However, due to the risk of brain swelling and bleeding (also known as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities), treatment with lecanemab involves frequent MRIs and neurology or geriatrics appointments to monitor for these abnormalities, which can be life threatening. So far, three patient deaths have potentially been tied to lecanemab.
It is likely that the FDA will grant is lecanemab traditional approval later this year, prompting Medicare to reconsider its current coverage restrictions and potentially enabling widespread use.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Dermatology, Eli Lilly, Immunotherapy / 18.05.2023
Lilly: Novel Monoclonal Antibody Shows Promise in Hard to Treat Facial and Hand Atopic Dermatitis
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lotus Mallbris, MD PhD
Dermatologist andSenior Vice President
Global Immunology Development and Medical Affairs
Lilly
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you briefly describe what is meant by atopic dermatitis and types treated in this study?
Response: First, this study specifically evaluated lebrikizumab, a novel, investigational, monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to interleukin 13 (IL-13) with high-affinity and high potency. Inflammation due to over-activation of the IL-13 pathway plays a central role in the pathogenesis of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, commonly called eczema.
This secondary analysis focused on patients treated with lebrikizumab from the 16-week induction periods of the ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2 studies and the ADhere study. In the trials, we assessed the presence or absence of face or hand dermatitis in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. If present at baseline, at 16 weeks, clinicians assessed the change from baseline on a scale of cleared, improved, no change, or worsened. Only patients with face and hand dermatitis were evaluated as part of the analysis.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Gastrointestinal Disease, Immunotherapy / 17.05.2023
Ulcerative Colitis: Lilly Reports Clinically Meaningful Response with Mirikizumab in Phase Two Study
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Marla Dubinsky, M.D.
Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine
Co-director of the Susan and Leonard Feinstein IBD Clinical Center
Chief of the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? How does MIRIKIZUMAB differ from other medications for UC?
Response: This is a phase 2 study to assess the PK (pharamcokinetics), safety and efficacy of mirikizumab in pediatric ulcerative colitis (UC).
Mirikizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the p19 subunit of interleukin-23, a key inflammatory mediator in inflammatory bowel disease.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Dermatology, JAMA / 15.05.2023
JAMA Dermatology Study Evaluates Nonsteroidal Roflumilast Foam for Seborrheic Dermatitis
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Matthew Zirwas, MD
Founder, Bexley Dermatology Research Clinic
Bexley, OH 43209
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? How does Roflumilast differ from other treatments for seb derm?
Response: Seborrheic dermatitis affects up to 5% of the population globally and can have major impacts on quality of life. Treatment regimens are often complicated given the association of seborrheic dermatitis to hair bearing areas of the body, requiring multiple treatments for different parts of the body. Our phase 2 study aimed to understand the efficacy and safety of once-daily roflumilast foam 0.3% in adults with seborrheic dermatitis on their scalp, face and trunk. Roflumilast foam is a selective and highly potent phosphodiesterase (PDE) 4 inhibition that is being studied for a range of inflammatory skin conditions.
(more…)
Allergies, Author Interviews, Pediatrics / 10.05.2023
NEJM: Viaskin Patch Shows Promising Results for Toddlers with Peanut Allergy
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Matthew Greenhawt, MD, MBA, MSc
Professor of Pediatrics
Section of Allergy and Immunology
Director, Food Challenge and Research Unit
Children’s Hospital Colorado
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Anschutz Medical Campus
Aurora, CO 80045
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Is the incidence of peanut allergy in toddlers stabilizing with the earlier introduction of peanuts?
Response: There exists an urgent unmet medical need for infants and toddlers living with peanut allergy. Peanut allergy affects approximately 2% of U.S. children and has been a growing public health problem over the past 20 years. In fact, the number of kids affected by peanut allergy has tripled in that time span. Peanut allergy is not likely to be naturally outgrown, and reactions can be severe.
However, there is hope. There is growing evidence that the allergic immune system is more modifiable early in life. The EPITOPE study evaluated Viaskin Peanut in children ages 1 – 3 years of age. Viaskin Peanut is an investigational epicutaneous immunotherapy (EPIT) product, which uses the skin as a route to desensitize a patient to be less reactive to peanut. This is a daily therapy, worn between the shoulders on the back, which allows for non-oral peanut desensitization, which many parents find highly appealing.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Infections, JAMA, NYU, USPSTF / 09.05.2023
USPSTF: High Risk Populations Should Be Screened for Latent Tuberculosis
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Gbenga Ogedegbe, MD, MPH
Dr. Adolph & Margaret Berger Professor of Population Health
Director, Division of Health & Behavior
Director Center for Healthful Behavior Change
Department of Population Health
NYU Langone Health
NYU School of Medicine
Member of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection that is spread through the air from one person to another and usually affects the lungs. It’s a significant public health concern in the U.S. People can be infected with TB bacteria but not have any symptoms or be contagious, which is known as a latent TB infection or LTBI. If LTBI is left untreated, it can progress to active TB, which can cause serious health problems and become contagious.
(more…)
Alzheimer's - Dementia, Author Interviews, JAMA, Mediterranean Diet, Mental Health Research / 08.05.2023
Adherence to MIND Diet May Reduce Risk of All-Cause Dementia
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Yuan Changzheng ScD, MSc, B.M.
Research Professor
Doctoral supervisor, School of Medicine
Zhejiang University School of Public Health
Adjunct assistant professor
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The prevention of all-cause dementia is important as it poses substantial burdens on healthcare systems and threatens the well-being of older adults, and lack of effective treatments makes its prevention crucial. The Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) diet is a hybrid of the Mediterranean diet and the DASH diet, and it emphasizes natural plant-based foods, limited intake of certain animal foods and foods high in saturated fat and encourages consumption of berries and green leafy vegetables rich in vitamins and antioxidants. The MIND diet has previously been associated with lower risk of Alzheimer's disease and slower cognitive decline but few studies have examined its association with all-cause dementia or AD with inconclusive results.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Breast Cancer, Cancer Research, JAMA, MRSA, Radiation Therapy / 06.05.2023
Bacterial Decolonization Reduced Radiation Dermatitis in Patients with Nasal Staphylococcus aureus
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Beth McLellan, M.D.
Chief, Division of Dermatology
Montefiore Medical Center
Albert Einstein College of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? How is the decolonization initiated and maintained?
Response: We were interested in exploring whether bacteria on the skin plays a role in radiation dermatitis like it does in other skin diseases that cause a breakdown in the skin barrier. We used a bacterial decolonization regimen that includes chlorhexidine 2% cleanser for the body and mupirocin 2% ointment to the inside of the nose for 5 consecutive days before starting radiation therapy and repeated for an additional 5 days every other week for the duration of radiation.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Diabetes, Gastrointestinal Disease / 04.05.2023
DDW23: Endoscopic ReCET Procedure Plus Semaglutide Eliminates Need for Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Celine B. E. Busch, Research Associate
Gastroenterology and Hepatology Standard PhD Candidate
Dr. Jacques Bergman
Professor, Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Amsterdam UMC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you describe the ReCET procedure?
Response: Currently more than 400 million people worldwide have type 2 diabetes (T2D) and these numbers are rapidly increasing. At the moment there is no treatment option available that effectively treats the root cause of T2D, i.e. insulin resistance, the increasing loss of response to our body’s own insulin. T2D is generally treated with drug therapy, yet drug therapy can be expensive, requires the patient to take their drugs every day, and at best “controls” the disease without actually resolving it. Despite the availability of many T2D drugs, less than 50% of all T2D have adequately controlled blood glucose levels.
The duodenum (the first part of the small bowel, immediately distal to the stomach) has proven to play a crucial role in glucose homeostasis in T2D. We know from bariatric surgery, that bypassing the duodenum by an Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass has an immediate and profound effect on T2D by improving the sensitivity to the body’s own insulin resistance. However, performing invasive bariatric surgery for many T2D is not feasible. But we can reach the duodenum easily via upper GI endoscopy.
ReCET is a single endoscopic procedure, performed under deep sedation. The ReCET catheter is advanced next to the scope, and once it is placed in the duodenum the flex circuit is unfolded until it touches the full circumference of the duodenum. The flex circuit contains the electrodes that create a pulsed electric field which “electroporates” the cells. Electroporation irreversibly makes small, that cause the cell to die of natural cell death, or apoptosis. This process can be precisely titrated for its depth of damage and does not generate heat thus avoiding damage to deeper wall layers, a major hurdle for standard endoscopic ablation techniques. The ReCET procedure lasts about 60 minutes to treat a 10-15 cm segment of the duodenum. The procedure does not cause significant side-effects and patients are discharged the same day.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Fertility / 02.05.2023
Insurance Mandates for Infertility Vary Widely from State to State
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Arshia Sandozi, DO, MPH
Urology Resident at Maimonides Medical Center
Interested in health disparities, equity, and policy
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Infertility affects 12-15% of heterosexual couples and can be a devastating diagnosis. Healthcare for infertility can be costly, and is not always covered by insurance. This is troubling because the median cost for a procedure like in vitro fertilization is more than nineteen thousand dollars per cycle and most people require more than one cycle before a live birth.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Health Care Systems, JAMA, Technology, UCSD / 01.05.2023
ChatGPT Provided Surprising Empathetic Answers to Patient Queries
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Zechariah Zhu, B.S.
Affiliate Scientist with the Qualcomm Institute at UC San Diego and study co-author
First author: John W. Ayers, PhD, MA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: In today’s day and age (especially after the COVID-19 pandemic), an increasing number of people are turning to virtual options for healthcare. Most notably, there was a 1.6-fold increase in electronic patient messages, which significantly increased the burden on physicians, with a record-high proportion of physicians (62%) reporting burnout symptoms.
On the other hand, we also see the rise of AI technologies like ChatGPT—an AI chatbot assistant that has taken the world by storm recently with its ability to provide lengthy response essays to many questions it is asked. Our objective for this study, then, was to evaluate the ability of ChatGPT to provide quality and empathetic responses to patient questions.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Kidney Stones, Lifestyle & Health, Urology / 29.04.2023
AUA23: Study Examines Whether Alkaline Water Drinks Really Provide Extra Anions
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Paul Piedras, BS
University of California, Irvin
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The consumption of alkaline water is gaining popularity among the public as a preferred method of hydration. A variety of reasons may be associated with this including that the general population may believe that drinking an alkalotic fluid will lead to a raise in systemic pH. Given that alkaline water is more expensive than spring water, we decided to further explore what effects it may have on urinary alkalization.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Dermatology, Melanoma, USPSTF / 27.04.2023
USPSTF Issues Skin Cancer Screening Statement
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
John M. Ruiz, Ph.D
Associate Professor of Clinical Psychology
Department of Psychology
University of Arizona
Dr. Ruiz is the incoming editor-in-chief of the American Psychological Association (APA) journal, Health Psychology
Dr. Ruiz joined the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in January 2022
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States, but it often does not cause serious complications or death. The Task Force’s recommendation on screening for skin cancer focuses on the effectiveness of visual skin exams for children and adults who do not have any symptoms. When reviewing the latest research, we found that there is currently not enough evidence to tell us whether or not screening people without signs or symptoms is beneficial. This is an I statement.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Diabetes, Weight Research / 27.04.2023
ADA Statement Regarding Lilly’s Announcement of Weight Loss in Adults with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes with Tirzepatide (Mounjaro™) Injections
Statement from Dr. Robert Gabbay, Chief Scientific and Medical Officer for the ADA, regarding the Lilly statement this of April...
Aging, Author Interviews, Emergency Care, Lifestyle & Health, Orthopedics / 26.04.2023
Dog Walking Sends Thousands to Emergency Rooms Each Year
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Ridge Maxson
M.D. Candidate, Class of 2024
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Dog walking is an increasingly popular mode of physical activity for adults in the US, but its injury burden and associated risk factors are not fully understood. This study found that the 3 most common injuries sustained by adult dog walkers in the US were finger fracture, TBI, and shoulder sprain or strain. Dog walking-related injuries sent approximately 423,000 adults to US EDs between 2001 and 2020, with an annual average of more than 21,000 visits. During that 20-year period, the estimated annual injury incidence increased by more than 4-fold. Among injured dog walkers, older adults and women were particularly vulnerable to serious injury, such as fracture and TBI.
(more…)
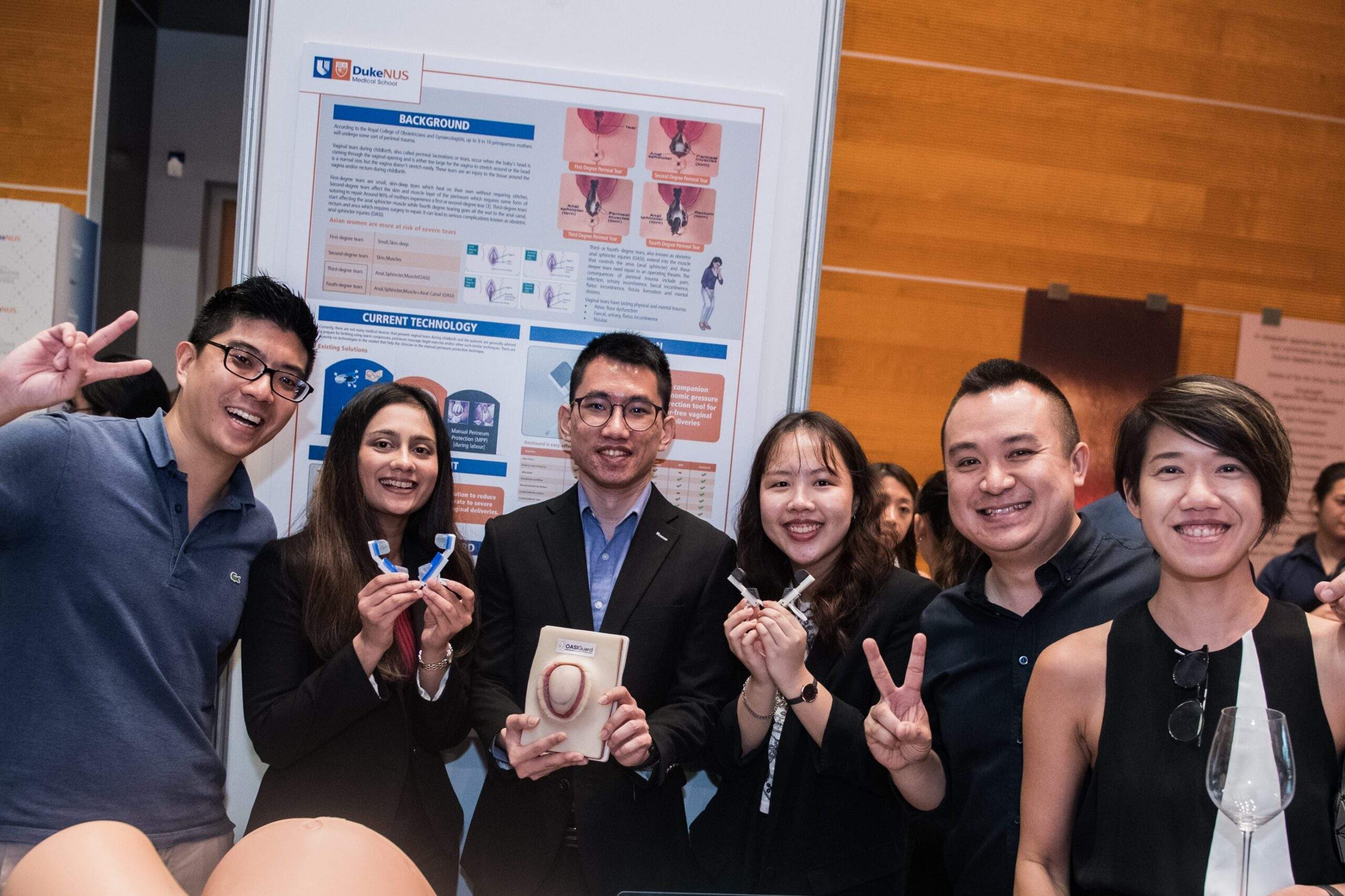
Author Interviews, Duke, OBGYNE / 26.04.2023
Duke-NUS Innovator Team Develops Tool to Reduce Vaginal Tears During Childbirth
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
TEAM FEMTECH
Feng Yi Low, MD student (Class of 2024), Duke-NUS Medical School
Casey Ang Fann Ting, Biomedical Engineering student, College of Design and Engineering, National University of Singapore (NUS)
Anar Sanjaykumar Kothary, MBA student, NUS Business School
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this innovation? What is the problem you sought to mitigate?
Response: A safe and low cost solution to reduce the incidence of moderate to severe vaginal tears during childbirth. Vaginal tears are a serious complication during delivery. 90% of women will experience it during childbirth. It is even more prominent in the Asian context as Asian women are 74% more likely to experience tearing due to various factors such as their skin composition as well as stature to name a few.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Breast Cancer, JAMA, Race/Ethnic Diversity / 25.04.2023
Breast Cancer Screening: One-Size-Fits-All Approach May Not be Optimal, Equitable or Fair
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Mahdi Fallah, MD, PhD
Study and Group Leader
Risk Adapted Prevention (RAD) Group
Division of Preventive Oncology
National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT)
German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ)
Heidelberg, Germany
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Breast cancer is a significant public health problem, being the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death in women in the US. Breast cancer screening from age 50 has been associated with a reduction in mortality and is recommended by the US Preventive Services Task Force. However, there is a significant disparity in mortality rates between Black and White individuals, with Black women having a higher death rate, especially before age 50. The current one-size-fits-all policy for breast cancer screening may not be equitable or optimal, and risk-adapted starting ages of screening based on known risk factors, such as race and ethnicity, may be recommended to optimize the benefit of screening. Our study aimed to provide evidence for a risk-adapted starting age of screening by race and ethnicity.
(more…)
Author Interviews / 25.04.2023
Thirteen-fold disparities between states in clozapine prescriptions to United States Medicaid patients
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Mariah W Panoussi, BS, MBS
Second-year medical student at Saba University School of Medicine, Saba, Dutch Caribbean
Department of Medical Education
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Scranton, PA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Clinical guidelines currently state that the atypical antipsychotic clozapine effectively treats patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS) 1. TRS occurs in up to one-third of patients with schizophrenia.2,3 However, there is evidence that demonstrates a lack of clozapine utilization by providers.2 This underutilization has been attributed to clozapine’s numerous adverse effects, in particular agranulocytosis.4 Other barriers include close monitoring for agranulocytosis, changes in administration and registry programs, as well as concerns regarding physician’s attitude toward and knowledge about clozapine.4,5 These barriers have thus caused a sizable variation in clozapine usage throughout the US. Using Medicaid data from 2015-2019, we conducted a secondary data analysis to examine the varied usage of clozapine in the US Medicaid programs.6
(more…)
Author Interviews, Urinary Tract Infections, Urology / 24.04.2023
Cochrane Review Finds Cranberries May Help Prevent Urinary Tract Infections
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr Jacqueline Stephens MPH, PhD
Epidemiologist & Senior lecturer
Flinders University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: An increase in the volume of evidence published in the peer-reviewed literature on this topic prompted an update of this Cochrane Review. (more…)
Author Interviews, COVID -19 Coronavirus, Herpes Viruses, HIV, HPV, Infections, STD / 24.04.2023
Thermo Fisher Scientific Works to Combat Risking STI Epidemic with Better, Faster Testing
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Manoj Gandhi, MD PhD
Senior Medical Director of Genetic Testing Services, Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Dr. Gandhi has been working to advance the quality of medical care globally. Using his knowledge of Clinical Medicine and Molecular Biology/Pathology, he is focused on bridging these two fields and bringing innovative solutions that help advance science, the practice of medicine with the ultimate goal of impacting patient lives, whether it be in Infectious Diseases or Oncology or Personalized Medicine. This approach allows him to explore creative ways to utilize technology to help better identify diseases and improve the direction and value of treatment.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the most common STIs prevalent in the US and worldwide today?
Response: By far, the most common STIs in the US and worldwide is Human Papillomavirus (HPV) that can cause cervical cancer in women and Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) that is the cause of genital herpes. Outside of these two major causes of STI, the others that are very common are Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Trichomoniasis and Syphilis. It is important to note that the reported cases represent only a subset of the individuals with an infection as many may be asymptomatic and could be spreading these STIs to others. HIV is another STI that is common but usually rests in its own category due to its impact.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Neurological Disorders, Parkinson's / 24.04.2023
Parkinson’s Disease: Extended Release Levodopa Tested to Reduce Motor Fluctuations
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Alberto J. Espay, MD, MSc, FAAN
Professor of Neurology
Director and Endowed Chair
Gardner Family Center for Parkinson's disease and Movement Disorders
University of Cincinnati Academic Health Center
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: This study was meant to address the gap that current oral levodopa formulations do not suffice to lessen motor fluctuations in people with Parkinson’s disease. IPX203 is a unique extended-release formulation of levodopa.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Cancer Research, JAMA, NCI, Ovarian Cancer / 21.04.2023
NCI Study Evaluates Aspirin Use with Ovarian Cancer Risk
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lauren Hurwitz, PhD
Postdoctoral Fellow
Division of Cancer Epidemiology & Genetics
National Cancer Institute
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Prior studies have demonstrated that frequent (i.e., daily or near daily) use of aspirin is associated with a lower risk of developing ovarian cancer. We sought to determine if this risk reduction is also observed for individuals with greater genetic susceptibility to ovarian cancer, who may benefit more from preventive interventions.
Our study found that individuals who took aspirin frequently had a lower risk of ovarian cancer, regardless of whether they had higher or lower genetic susceptibility to ovarian cancer.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Genetic Research, PNAS, UCSD / 20.04.2023
We Are Able to See Thanks to a Protein Acquired from Bacteria
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Chinmay Kalluraya
a Selma and Robert Silagi Award for Undergraduate Excellence winner
UC San Diego and now a graduate student at MIT
and
Matt Daugherty Ph.D
Associate Professor
University of California, San Diego
Department of Molecular Biology, School of Biological Sciences
La Jolla CA, 92093-0377
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you explain the role of retinoid-binding protein?
 Response: We were broadly interested in discovering instances of bacterial genes that have been acquired by diverse animal genomes over millions of years of evolution by the process of horizontal gene transfer (HGT). Since these events are quite rare and most previous discoveries have been serendipitous, we developed computational methods to identify genes acquired by HGT in animals. One of the exciting discoveries from our work was that vertebrate IRBP appeared to have originated in bacteria and is now a critical component of the vertebrate visual cycle, so this paper focuses on that one discovery.
IRBP or interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein is an important protein present in the space between two major cell types in our eyes, photoreceptor cells and RPE cells. Our ability to see involves an intricate set of steps where light is first sensed by causing a change (isomerization) in the chemical structure of molecules in the eye called retinoids. This sensing of light occurs in our photoreceptor cells. Following this change in the chemical structure, the retinoid needs to be recycled back to the chemical structure that can again sense light. This recycling occurs in RPE cells. IRBP performs the essential function of shuttling retinoids between the photoreceptors and the RPE cells, which allows the cycle of sensing and regeneration to work. Supporting its importance, mutations in IRBP (also known as retinol binding protein 3 or RBP3) can cause several severe human eye diseases.
(more…)
Response: We were broadly interested in discovering instances of bacterial genes that have been acquired by diverse animal genomes over millions of years of evolution by the process of horizontal gene transfer (HGT). Since these events are quite rare and most previous discoveries have been serendipitous, we developed computational methods to identify genes acquired by HGT in animals. One of the exciting discoveries from our work was that vertebrate IRBP appeared to have originated in bacteria and is now a critical component of the vertebrate visual cycle, so this paper focuses on that one discovery.
IRBP or interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein is an important protein present in the space between two major cell types in our eyes, photoreceptor cells and RPE cells. Our ability to see involves an intricate set of steps where light is first sensed by causing a change (isomerization) in the chemical structure of molecules in the eye called retinoids. This sensing of light occurs in our photoreceptor cells. Following this change in the chemical structure, the retinoid needs to be recycled back to the chemical structure that can again sense light. This recycling occurs in RPE cells. IRBP performs the essential function of shuttling retinoids between the photoreceptors and the RPE cells, which allows the cycle of sensing and regeneration to work. Supporting its importance, mutations in IRBP (also known as retinol binding protein 3 or RBP3) can cause several severe human eye diseases.
(more…)
 Response: We were broadly interested in discovering instances of bacterial genes that have been acquired by diverse animal genomes over millions of years of evolution by the process of horizontal gene transfer (HGT). Since these events are quite rare and most previous discoveries have been serendipitous, we developed computational methods to identify genes acquired by HGT in animals. One of the exciting discoveries from our work was that vertebrate IRBP appeared to have originated in bacteria and is now a critical component of the vertebrate visual cycle, so this paper focuses on that one discovery.
IRBP or interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein is an important protein present in the space between two major cell types in our eyes, photoreceptor cells and RPE cells. Our ability to see involves an intricate set of steps where light is first sensed by causing a change (isomerization) in the chemical structure of molecules in the eye called retinoids. This sensing of light occurs in our photoreceptor cells. Following this change in the chemical structure, the retinoid needs to be recycled back to the chemical structure that can again sense light. This recycling occurs in RPE cells. IRBP performs the essential function of shuttling retinoids between the photoreceptors and the RPE cells, which allows the cycle of sensing and regeneration to work. Supporting its importance, mutations in IRBP (also known as retinol binding protein 3 or RBP3) can cause several severe human eye diseases.
(more…)
Response: We were broadly interested in discovering instances of bacterial genes that have been acquired by diverse animal genomes over millions of years of evolution by the process of horizontal gene transfer (HGT). Since these events are quite rare and most previous discoveries have been serendipitous, we developed computational methods to identify genes acquired by HGT in animals. One of the exciting discoveries from our work was that vertebrate IRBP appeared to have originated in bacteria and is now a critical component of the vertebrate visual cycle, so this paper focuses on that one discovery.
IRBP or interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein is an important protein present in the space between two major cell types in our eyes, photoreceptor cells and RPE cells. Our ability to see involves an intricate set of steps where light is first sensed by causing a change (isomerization) in the chemical structure of molecules in the eye called retinoids. This sensing of light occurs in our photoreceptor cells. Following this change in the chemical structure, the retinoid needs to be recycled back to the chemical structure that can again sense light. This recycling occurs in RPE cells. IRBP performs the essential function of shuttling retinoids between the photoreceptors and the RPE cells, which allows the cycle of sensing and regeneration to work. Supporting its importance, mutations in IRBP (also known as retinol binding protein 3 or RBP3) can cause several severe human eye diseases.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Education, Pediatrics / 19.04.2023
Study Uses Visual Attention to Assess How Young Children Learn New Words
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Larissa K. Samuelson, PhD
Professor
Developmental Dynamics Lab
School of Psychology; UK 14th for Research Quality
Psychology, Psychiatry, and Neuroscience
University of East Anglia, United Kingdom
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Words direct the attention of infants, children and adults to mentioned objects in the environment. When someone says “Can you find the candy,” you look to the candy sitting on the counter. This fact is the basis of many tests of infant cognition in laboratories. To find out if a child knows the word “bike” we put a picture of a bike and a truck on a TV screen, say the word “bike” and see if they look at the correct object.
There is also evidence that words can direct attention even if you don’t know what they mean yet. For example, in studies of learning in the lab novel made up words like “modi” can direct children’s attention to specific features of objects. One particular example of this is the “shape bias”. If a two-year-old is shown a novel object and told a novel name, for example “This is my blicket,” and then asked, “Can you get your blicket” and shown one object that matches the named one in shape and another that is made from the same material, they will attend to the one that matches in shape. Researchers think the naming event “This is my…” cues children to look at things that are the same shape because they already know many names for things in sets that are similar in shape; cups are all cup-shaped, keys are all key-shaped, spoons are all spoon-shaped, etc.
Prior research suggests there may be differences in the way children who struggle with language decide what a new word means. For example, children with Developmental Language Disorder do not pay attention to the same things when learning new words as children with typical language development. These children do not look to an object that matches a named exemplar in shape when asked to “get your blicket”. But you can’t diagnose children with DLD until they are 3 or 4. We want to see if we can identify these children earlier, so they can get early support.
(more…)
Larissa K. Samuelson, PhD
Professor
Developmental Dynamics Lab
School of Psychology; UK 14th for Research Quality
Psychology, Psychiatry, and Neuroscience
University of East Anglia, United Kingdom
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Words direct the attention of infants, children and adults to mentioned objects in the environment. When someone says “Can you find the candy,” you look to the candy sitting on the counter. This fact is the basis of many tests of infant cognition in laboratories. To find out if a child knows the word “bike” we put a picture of a bike and a truck on a TV screen, say the word “bike” and see if they look at the correct object.
There is also evidence that words can direct attention even if you don’t know what they mean yet. For example, in studies of learning in the lab novel made up words like “modi” can direct children’s attention to specific features of objects. One particular example of this is the “shape bias”. If a two-year-old is shown a novel object and told a novel name, for example “This is my blicket,” and then asked, “Can you get your blicket” and shown one object that matches the named one in shape and another that is made from the same material, they will attend to the one that matches in shape. Researchers think the naming event “This is my…” cues children to look at things that are the same shape because they already know many names for things in sets that are similar in shape; cups are all cup-shaped, keys are all key-shaped, spoons are all spoon-shaped, etc.
Prior research suggests there may be differences in the way children who struggle with language decide what a new word means. For example, children with Developmental Language Disorder do not pay attention to the same things when learning new words as children with typical language development. These children do not look to an object that matches a named exemplar in shape when asked to “get your blicket”. But you can’t diagnose children with DLD until they are 3 or 4. We want to see if we can identify these children earlier, so they can get early support.
(more…)
 Larissa K. Samuelson, PhD
Professor
Developmental Dynamics Lab
School of Psychology; UK 14th for Research Quality
Psychology, Psychiatry, and Neuroscience
University of East Anglia, United Kingdom
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Words direct the attention of infants, children and adults to mentioned objects in the environment. When someone says “Can you find the candy,” you look to the candy sitting on the counter. This fact is the basis of many tests of infant cognition in laboratories. To find out if a child knows the word “bike” we put a picture of a bike and a truck on a TV screen, say the word “bike” and see if they look at the correct object.
There is also evidence that words can direct attention even if you don’t know what they mean yet. For example, in studies of learning in the lab novel made up words like “modi” can direct children’s attention to specific features of objects. One particular example of this is the “shape bias”. If a two-year-old is shown a novel object and told a novel name, for example “This is my blicket,” and then asked, “Can you get your blicket” and shown one object that matches the named one in shape and another that is made from the same material, they will attend to the one that matches in shape. Researchers think the naming event “This is my…” cues children to look at things that are the same shape because they already know many names for things in sets that are similar in shape; cups are all cup-shaped, keys are all key-shaped, spoons are all spoon-shaped, etc.
Prior research suggests there may be differences in the way children who struggle with language decide what a new word means. For example, children with Developmental Language Disorder do not pay attention to the same things when learning new words as children with typical language development. These children do not look to an object that matches a named exemplar in shape when asked to “get your blicket”. But you can’t diagnose children with DLD until they are 3 or 4. We want to see if we can identify these children earlier, so they can get early support.
(more…)
Larissa K. Samuelson, PhD
Professor
Developmental Dynamics Lab
School of Psychology; UK 14th for Research Quality
Psychology, Psychiatry, and Neuroscience
University of East Anglia, United Kingdom
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Words direct the attention of infants, children and adults to mentioned objects in the environment. When someone says “Can you find the candy,” you look to the candy sitting on the counter. This fact is the basis of many tests of infant cognition in laboratories. To find out if a child knows the word “bike” we put a picture of a bike and a truck on a TV screen, say the word “bike” and see if they look at the correct object.
There is also evidence that words can direct attention even if you don’t know what they mean yet. For example, in studies of learning in the lab novel made up words like “modi” can direct children’s attention to specific features of objects. One particular example of this is the “shape bias”. If a two-year-old is shown a novel object and told a novel name, for example “This is my blicket,” and then asked, “Can you get your blicket” and shown one object that matches the named one in shape and another that is made from the same material, they will attend to the one that matches in shape. Researchers think the naming event “This is my…” cues children to look at things that are the same shape because they already know many names for things in sets that are similar in shape; cups are all cup-shaped, keys are all key-shaped, spoons are all spoon-shaped, etc.
Prior research suggests there may be differences in the way children who struggle with language decide what a new word means. For example, children with Developmental Language Disorder do not pay attention to the same things when learning new words as children with typical language development. These children do not look to an object that matches a named exemplar in shape when asked to “get your blicket”. But you can’t diagnose children with DLD until they are 3 or 4. We want to see if we can identify these children earlier, so they can get early support.
(more…)
AACR, Author Interviews, Cancer Research / 18.04.2023
AACR23: Phase 1 trial of IO-108, an antagonist antibody targeting LILRB2 (ILT4), as monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab in adult patients with advanced relapsed or refractory solid tumors
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Matthew H. Taylor, MD
Earle A. Chiles Research Institute
Providence Cancer Institute
Portland, OR
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What is the importance of ILT4 or LILRB2 in tumor growth?
- ILT4, also known as LILRB2, is expressed on myeloid cells, including monocytes, DCs, macrophages and neutrophils. LILRB2 expressing myeloid cells promote tumor immune evasion and contribute to anti-PD1 resistance, making this a promising target to reverse myeloid-mediated immune suppression in the TME.
- IO-108 is a fully human IgG4 therapeutic antibody that binds to LILRB2 with high affinity and specificity, and blocks binding of LILRB2 to multiple cancer-relevant ligands. This blockade causes re-programming of immune suppressive myeloid cells to pro-inflammatory in the tumor microenvironment leading to the activation of T cells.
- This first-in-human, open-label Phase 1 study of IO-108 as monotherapy or in combination with pembrolizumab was designed to learn about safety, tolerability and preliminary efficacy of IO-108 as monotherapy or in combination with a PD-1 inhibitor in patients with advanced, metastatic solid tumors. The study was also designed to find a dose of IO-108 that is safe and efficacious to be tested in patients with various solid tumors.
Author Interviews, COVID -19 Coronavirus, Diabetes, JAMA / 18.04.2023
COVID Linked to Higher Risk of New Onset Diabetes
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: [caption id="attachment_60303" align="alignleft" width="150"] Dr. Zafar Janjua[/caption] Naveed Zafar Janjua, MBBS, MSc, DrPH Executive Director, Data and Analytic Services BC Centre...
ADHD, Author Interviews, JAMA, Pediatrics, University of Michigan / 18.04.2023
Misuse of Prescription Stimulants Highly Variable Among US Schools
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Sean Esteban McCabe, PhD
Director, Center for the Study of Drugs, Alcohol, Smoking and Health
Department of Health Behavior and Biological Sciences
University of Michigan School of Nursing
Ann Arbor, MI
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Prescription stimulant therapy for ADHD helps millions of people, including in my own family, and students, friends and colleagues. It's critical to balance the need for access to these medications while reducing the risk for misuse. This is more important than ever now because there have been recent increases in the prescribing of stimulant therapy for ADHD. There is a need to understand the prevalence of stimulant therapy for ADHD and prescription stimulant misuse in U.S. middle and high schools.
(more…)