MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Reza Ghiasvand, PhD
Oslo Centre for Biostatistics and Epidemiology
Faculty of Medicne
University of Oslo
Oslo, Norway
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
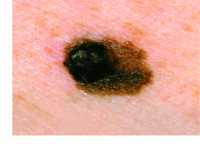
Response: Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. It is estimated that about 288,000 individuals will be diagnosed and about 61,000 will die from it in 2018, with the majority of patients in Australia, New Zealand, Europe and North America. Ultraviolet (UV) exposure (from both the sun and tanning beds) is the most important preventable risk factor for melanoma. However, the association between UV exposure and melanoma is complex and does not accord with a simple model in which risk increases directly with exposure. An individual risk of melanoma also depends on personal characteristics such as skin color and skin sensitivity to the UV exposure, hair color, number of moles, and age.
It has been hypothesized that the pattern of UV exposure may play a role in melanoma development in different body sites. For example, melanoma on the trunk (chest and back) has been linked to the recreational UV exposure such as sunbathing and frequent sunburns in people with high number of moles on their body. In contrast, melanomas on the head and neck have been linked to constant sun exposure such as occupational UV exposure, mainly in older people. Epidemiologic and molecular evidence in support of this hypothesis has been published based on analyses of small datasets. Also, melanoma on legs and arms is less studied under this hypothesis.
In our study, we examined UV exposure (sunbathing, sunburn and
sunbed use) and pigmentary factors (skin, eye, and hair color, freckling, and number of moles), and risk of melanoma on different body sites. We used information from the Norwegian Women and Cancer Study, a population-based cohort study that started in 1991, and includes more than 161,000 Norwegian women followed for an average of 18 years.
(more…)