Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Cancer Patients Benefit From Comprehensive Treatment Strategy
Sustaining Physical Activity With Age Decreases All-Cause Mortality Risk
 Trine Moholdt, PhD
Research Fellow
Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging | Exercise, Cardiometabolic Health and Reproduction
Norwegian University of Science and Technology
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Although obese individuals have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, evidence from many observational studies shows that in those who already have cardiovascular disease, being overweight or obese is associated with lower risk of mortality compared to their normal weight counterparts.
This phenomenon is often called the “obesity paradox”. Recently we observed that in individuals who have a high physical activity level, there is no such obesity paradox and body mass index did not associate with survival time in those who with high physical activity (Moholdt et al, American Journal of Medicine, 2017). (more…)
Trine Moholdt, PhD
Research Fellow
Department of Circulation and Medical Imaging | Exercise, Cardiometabolic Health and Reproduction
Norwegian University of Science and Technology
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Although obese individuals have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, evidence from many observational studies shows that in those who already have cardiovascular disease, being overweight or obese is associated with lower risk of mortality compared to their normal weight counterparts.
This phenomenon is often called the “obesity paradox”. Recently we observed that in individuals who have a high physical activity level, there is no such obesity paradox and body mass index did not associate with survival time in those who with high physical activity (Moholdt et al, American Journal of Medicine, 2017). (more…)AI Trained Computer Program Can Monitor Health Forums To Detect Adverse Drug Reactions
Focusing On Employment Early Improves Success In Veterans with PTSD
Selfies Distort Your Face and Make Your Nose Look Bigger
Labor Costs Account For Largest Percentage of Operating Room Expenses
Collaborative Heart Failure Care Did Not Reduce Hospitalizations or Mortality, But Reduced Depression and Fatigue
This study evaluated the effect of a team intervention, Collaborative Care to Alleviate Symptoms and Adjust to Illness, also called CASA, on several aspects of quality of life in 314 patients with heart failure. The patients, who received care at diverse health systems in Colorado, were randomized to receive usual care or usual care supplemented with the CASA intervention, which included a nurse and a social worker who collaborated with a primary care provider, cardiologist, and palliative care physician to address the patients’ needs.
The study found that the CASA intervention did not influence the primary outcome of heart failure health status, yet did improve patients’ depression and fatigue. CASA did not influence number of patient hospitalizations or mortality. (more…)
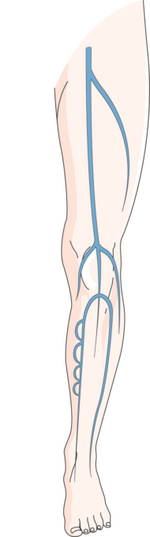
Varicose Veins Associated With Increased Risk of Deep Vein Blood Clots
Decision Aids Can Help Heart Failure Patients Determine If They Want an LVAD
Standardization and Collaboration Reduced Use of Costly CRRT Treatment for Critically Ill Patients
Heart Attacks Rarely Misdiagnosed in Emergency Rooms
 Daniel A. Waxman, MD, PhD
Department of Emergency Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine
University of California, Los Angeles
RAND Corporation Santa Monica, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: When people talk about medical error, they are usually referring to treatment error—giving the wrong medication, operating on the wrong side of the body, etc. But many believe that diagnostic error—the failure to diagnose a condition when a patient seeks care—is at least as widespread and consequential a problem. However, diagnostic errors are intrinsically difficult to measure, since one can rarely prove that a condition was present at the time it was not diagnosed.
In this study, we introduce a novel method for measuring how often patients who come to the emergency room with symptoms of an imminent cardiovascular emergency such as acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) are discharged home without a diagnosis.
We find that among Medicare patients whose ER visits were attributable to symptoms of an imminent infarction, only about 2.3% were discharged home, and that the figure was under 5% for each of the other four conditions we studied. However, we also found that these relatively low rates did not improve between 2007 and 2014.
(more…)
Daniel A. Waxman, MD, PhD
Department of Emergency Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine
University of California, Los Angeles
RAND Corporation Santa Monica, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: When people talk about medical error, they are usually referring to treatment error—giving the wrong medication, operating on the wrong side of the body, etc. But many believe that diagnostic error—the failure to diagnose a condition when a patient seeks care—is at least as widespread and consequential a problem. However, diagnostic errors are intrinsically difficult to measure, since one can rarely prove that a condition was present at the time it was not diagnosed.
In this study, we introduce a novel method for measuring how often patients who come to the emergency room with symptoms of an imminent cardiovascular emergency such as acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) are discharged home without a diagnosis.
We find that among Medicare patients whose ER visits were attributable to symptoms of an imminent infarction, only about 2.3% were discharged home, and that the figure was under 5% for each of the other four conditions we studied. However, we also found that these relatively low rates did not improve between 2007 and 2014.
(more…)Despite Advancing Neonatal Health, Preterm Babies Still Risk Cognitive Impairment
USPSTF: Ovarian Cancer Screening Not Recommended in Low-Risk, Asymptomatic Women
Study Finds No Benefit To Prophylactic Haldol For Delirium in ICU
 Mark van den Boogaard, PhD, RN, CCRN
Assistant Professor
Department of Intensive Care Medicine
Radboud University Medical Center
Nijmegen Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Delirium is affecting many of our intensive care unit (ICU) patients which is impacting their recovery on the short-term as well as on the long-term. Therefore we were very interested to investigate if the use prophylactic haloperidol would be beneficial for the ICU patients. Especially because there were indications that it would be effective in ICU delirium prevention and also because this drug is being used in daily practice to prevent ICU delirium although there is no clear evidence. The overall finding of our large-scale well designed study is that we didn’t find any beneficial effect of prophylactic haloperidol in ICU patients. Moreover, this finding is very consistent over all groups of patients. (more…)
Mark van den Boogaard, PhD, RN, CCRN
Assistant Professor
Department of Intensive Care Medicine
Radboud University Medical Center
Nijmegen Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Delirium is affecting many of our intensive care unit (ICU) patients which is impacting their recovery on the short-term as well as on the long-term. Therefore we were very interested to investigate if the use prophylactic haloperidol would be beneficial for the ICU patients. Especially because there were indications that it would be effective in ICU delirium prevention and also because this drug is being used in daily practice to prevent ICU delirium although there is no clear evidence. The overall finding of our large-scale well designed study is that we didn’t find any beneficial effect of prophylactic haloperidol in ICU patients. Moreover, this finding is very consistent over all groups of patients. (more…)Despite Promise, EMRs Have Not Reduced Administrative or Billing Expenses
Despite Safe Sleeping Recommendations, Infant Suffocations Continue To Rise
Bariatric Surgery Associated With Reduced Need For Diabetes Medications at Six Years
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Dr Jérémie Thereauz Praticien Hospitalier Chirurgie viscérale et digestive MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main...
Aggressive Systolic Blood Pressure Control In Older Patients With HFpEF Should Be Avoided
 MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Apostolos Tsimploulis, Chief Medical Resident
Dr. Phillip H. Lam, Chief Cardiology Fellow
The Washington, DC Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Georgetown University, and
MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Hypertension is a major risk factor for the development of new heart failure (HF). Findings from multiple randomized controlled trials in hypertension have consistently demonstrated that controlling systolic blood pressure (SBP) to normal levels such as to SBP <120 mm Hg reduces the risk of developing new HF.
However, interestingly, once patients develop heart failure, those with a normal SBP value such as SBP <120 mm Hg tend to have poor outcomes. This paradoxical association – also called reverse epidemiology – although poorly understood – has been described with other HF risk factors such as smoking and obesity. Regarding poor outcomes associated with lower SBP in HF patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF – pronounced Hef-ref), it has been suggested that it may be a marker of weak heart muscle that is unable to pump enough blood. However, less is known about this association in patients with HF and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF – pronounced Hef-pef) –– the heart muscle is not weak in the traditional sense.
This is an important question for a number of reasons: nearly half of all heart failure patients have HFpEF which accounts for about 2.5 to 3 million Americans. These patients have a high mortality similar to those with HFrEF – but unlike in HFrEF few drugs have been shown to improve their outcomes. Thus, there is a great deal of interest in improving their outcomes. One of those approaches is to control . systolic blood pressure and the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update of the HF guidelines recommend that SBP “should be controlled in patients with HFpEF in accordance with published clinical practice guidelines to prevent morbidity.”
Thus, our study was designed to answer that simple question: do patients with HFpEF and SBP <120 mmHg, which is considered to be normal SBP, have better outcomes than those with SBP ≥120 mmHg.
Using a sophisticated approach called propensity score matching we assembled two groups of patients with HFpEF – one group with SBP <120 mmHg and the other groups had SBP ≥120 mmHg – and patients in both groups were similar in terms of 58 key baseline characteristics. In this population of balanced patients with HFpEF, those with a normal systolic blood pressure had a higher risk of mortality – starting 30 days post-discharge up to about 6 years. Finding from our restricted cubic spline plots suggest that compared with SBP <120 mm Hg, SBP values ≥120 mm Hg (up to 200 mm Hg) was not associated with a higher risk of death.
(more…)
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Apostolos Tsimploulis, Chief Medical Resident
Dr. Phillip H. Lam, Chief Cardiology Fellow
The Washington, DC Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Georgetown University, and
MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Hypertension is a major risk factor for the development of new heart failure (HF). Findings from multiple randomized controlled trials in hypertension have consistently demonstrated that controlling systolic blood pressure (SBP) to normal levels such as to SBP <120 mm Hg reduces the risk of developing new HF.
However, interestingly, once patients develop heart failure, those with a normal SBP value such as SBP <120 mm Hg tend to have poor outcomes. This paradoxical association – also called reverse epidemiology – although poorly understood – has been described with other HF risk factors such as smoking and obesity. Regarding poor outcomes associated with lower SBP in HF patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF – pronounced Hef-ref), it has been suggested that it may be a marker of weak heart muscle that is unable to pump enough blood. However, less is known about this association in patients with HF and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF – pronounced Hef-pef) –– the heart muscle is not weak in the traditional sense.
This is an important question for a number of reasons: nearly half of all heart failure patients have HFpEF which accounts for about 2.5 to 3 million Americans. These patients have a high mortality similar to those with HFrEF – but unlike in HFrEF few drugs have been shown to improve their outcomes. Thus, there is a great deal of interest in improving their outcomes. One of those approaches is to control . systolic blood pressure and the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update of the HF guidelines recommend that SBP “should be controlled in patients with HFpEF in accordance with published clinical practice guidelines to prevent morbidity.”
Thus, our study was designed to answer that simple question: do patients with HFpEF and SBP <120 mmHg, which is considered to be normal SBP, have better outcomes than those with SBP ≥120 mmHg.
Using a sophisticated approach called propensity score matching we assembled two groups of patients with HFpEF – one group with SBP <120 mmHg and the other groups had SBP ≥120 mmHg – and patients in both groups were similar in terms of 58 key baseline characteristics. In this population of balanced patients with HFpEF, those with a normal systolic blood pressure had a higher risk of mortality – starting 30 days post-discharge up to about 6 years. Finding from our restricted cubic spline plots suggest that compared with SBP <120 mm Hg, SBP values ≥120 mm Hg (up to 200 mm Hg) was not associated with a higher risk of death.
(more…)Paid Family and Childbearing Leave Policies at Top US Medical Schools Found Lacking
More Car Crashes on 4/20 Marijuana Celebration Day
 Dr. John A Staples
MD, FRCPC, MPH
Scientist, Centre for Health Evaluation and Outcome Sciences
Clinical Assistant Professor
University of British Columbia
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Around 64 million Americans live in states that have legalized recreational marijuana. Many policymakers are trying to figure out what that means for traffic safety.
On April 20th, some Americans participate in an annual "4/20" counterculture holiday that celebrates and promotes the use of cannabis. Some 4/20 events such as those in Denver and San Francisco involve thousands of participants. Much like celebrations at midnight on New Year's eve, public 4/20 events sometimes mark 4:20 p.m. by a countdown followed by synchronized mass consumption of cannabis. We thought this was a perfect natural experiment to evaluate the influence that cannabis intoxication has on the risk of motor vehicle crash.
To examine this question, we analyzed 25 years of data on all fatal traffic crashes in the United States. We compared the number of drivers in crashes between 4:20 p.m. and midnight on April 20th to the number of drivers in crashes during the same time interval on control days one week earlier and one week later.
We found that the risk of crash involvement was 12% higher on April 20th than on control days. In the subgroups of drivers younger than 21 years of age, the risk of crash involvement was 38% higher on April 20th than on control days.
Assuming fewer than 12% of Americans celebrate 4/20, our results suggest that substance use at April 20th celebrations more than doubles the risk of fatal crash.
(more…)
Dr. John A Staples
MD, FRCPC, MPH
Scientist, Centre for Health Evaluation and Outcome Sciences
Clinical Assistant Professor
University of British Columbia
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Around 64 million Americans live in states that have legalized recreational marijuana. Many policymakers are trying to figure out what that means for traffic safety.
On April 20th, some Americans participate in an annual "4/20" counterculture holiday that celebrates and promotes the use of cannabis. Some 4/20 events such as those in Denver and San Francisco involve thousands of participants. Much like celebrations at midnight on New Year's eve, public 4/20 events sometimes mark 4:20 p.m. by a countdown followed by synchronized mass consumption of cannabis. We thought this was a perfect natural experiment to evaluate the influence that cannabis intoxication has on the risk of motor vehicle crash.
To examine this question, we analyzed 25 years of data on all fatal traffic crashes in the United States. We compared the number of drivers in crashes between 4:20 p.m. and midnight on April 20th to the number of drivers in crashes during the same time interval on control days one week earlier and one week later.
We found that the risk of crash involvement was 12% higher on April 20th than on control days. In the subgroups of drivers younger than 21 years of age, the risk of crash involvement was 38% higher on April 20th than on control days.
Assuming fewer than 12% of Americans celebrate 4/20, our results suggest that substance use at April 20th celebrations more than doubles the risk of fatal crash.
(more…)Distance to Trauma Center & Prehospital Care Influence Outcomes from Injuries
With or Without Reconstruction, Hard To Predict How You Will Feel After Mastectomy
 Dr. Clara Nan-hi Lee, MD
Comprehensive Cancer Center
The Ohio State University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The decision about breast reconstruction is very challenging because it’s unfamiliar, involves complex risk information, affects very personal concerns, and happens at a stressful time. One of the challenges is to predict how one will feel after the surgery. We know from psychology research that people often mis-predict their future emotions. So we were interested to see how well women predict their future well being after surgery.
The main findings are that patients having mastectomy without reconstruction believed they would be less satisfied than they turned out to be. And patients having mastectomy with reconstruction believed they would be more satisfied than they turned out to be. (more…)
Dr. Clara Nan-hi Lee, MD
Comprehensive Cancer Center
The Ohio State University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The decision about breast reconstruction is very challenging because it’s unfamiliar, involves complex risk information, affects very personal concerns, and happens at a stressful time. One of the challenges is to predict how one will feel after the surgery. We know from psychology research that people often mis-predict their future emotions. So we were interested to see how well women predict their future well being after surgery.
The main findings are that patients having mastectomy without reconstruction believed they would be less satisfied than they turned out to be. And patients having mastectomy with reconstruction believed they would be more satisfied than they turned out to be. (more…)First Signs of Psychotic Disorder May Appear in Childhood With Drop in IQ
Vancouver Study: 100% of Opioid-Users Tested Positive for Fentanyl
 William G. Honer, MD, FRCPC, FCAHS
Jack Bell Chair in Schizophrenia
Professor and Head, Department of Psychiatry
University of British Columbia
Vancouver, BC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The Province of British Columbia, Canada, has experienced a tremendous increase in the number of opioid related overdoses and deaths. In 2012, there were 269 drug overdose deaths, five years later in 2017 the overdose deaths are predicted to have increased 500%. Toxicology studies of deaths, and examination of seized drugs indicate fentanyl is the major cause.
These indirect measures suggest widespread exposure to fentanyl in opioid users, however direct studies of the extent of exposure of opioid users to fentanyl in the community are lacking. We carried out a community-based, longitudinal study using fentanyl testing in urine samples from volunteer participants. (It is called the “Hotel Study” since many of the participants live, or have lived in single room occupancy hotels) (more…)
William G. Honer, MD, FRCPC, FCAHS
Jack Bell Chair in Schizophrenia
Professor and Head, Department of Psychiatry
University of British Columbia
Vancouver, BC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The Province of British Columbia, Canada, has experienced a tremendous increase in the number of opioid related overdoses and deaths. In 2012, there were 269 drug overdose deaths, five years later in 2017 the overdose deaths are predicted to have increased 500%. Toxicology studies of deaths, and examination of seized drugs indicate fentanyl is the major cause.
These indirect measures suggest widespread exposure to fentanyl in opioid users, however direct studies of the extent of exposure of opioid users to fentanyl in the community are lacking. We carried out a community-based, longitudinal study using fentanyl testing in urine samples from volunteer participants. (It is called the “Hotel Study” since many of the participants live, or have lived in single room occupancy hotels) (more…)Potentially Cancerous Genital Lesions Common in Transplant Population
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Christina Lee Chung, MD Associate Professor Department of Dermatology Drexel University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: In early 2016, five years after the inception of our specialty medical-surgical transplant dermatology center, we realized our nonwhite transplant patients were developing skin cancer at higher rates and found interesting trends. These data were published in a previous manuscript. One of the more striking findings was that these patients were developing a high proportion of skin cancer in non-sun-exposed areas such as the genital region. There are no standard guidelines regarding genital skin evaluation and it is unclear how often it is performed in any capacity amongst dermatologists, including practitioners in our center, quite frankly. Our group was concerned that we could be missing skin cancers in this “hidden” area in our high-risk organ transplant population so we launched a quality improvement initiative that incorporated thorough genital skin evaluation as a standard part of post-transplant skin cancer screening.
Fifteen months after we started this modified screening process, we decided to evaluate the results. To account for any variation in examination, we looked at the findings of a single practitioner. We found that genital lesions are common in the transplant population and include high rates of genital warts and skin cancer. However, patient awareness of the presence of genital lesions was alarmingly low. Nonwhite transplant patients, Black transplant recipients in particular, were disproportionately affected by both genital warts and genital skin cancer in our cohort. Similar to cervical cancer, high-risk HPV types were closely associated with genital squamous cell carcinoma development in our transplant population. (more…)
Rate of Breast Biopsy After Cancer Treatment Relatively Low, and Most Are Benign
Clinical Pharmacist Intervention Can Reduce ED Visits and Hospital Readmissions
 Lene Vestergaard Ravn-Nielsen, MSc(Pharm)
Hospital Pharmacy of Funen
Clinical Pharmacy Department
Odense University Hospital
Odense, Denmark
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hospital readmissions are common among patients receiving multiple medication, with considerable costs to the patients and society.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: A multifaceted clinical pharmacist intervention can reduce ED visits and hospital readmissions. (more…)
Lene Vestergaard Ravn-Nielsen, MSc(Pharm)
Hospital Pharmacy of Funen
Clinical Pharmacy Department
Odense University Hospital
Odense, Denmark
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hospital readmissions are common among patients receiving multiple medication, with considerable costs to the patients and society.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: A multifaceted clinical pharmacist intervention can reduce ED visits and hospital readmissions. (more…)Study Finds Pulmonary Embolus Rarely the Cause of Syncope
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Acute Brain Lesions on MRI Can Predict Delayed Sequelae
 Won Young Kim, MD PhD
Department of Emergency Medicine
Asan Medical Center
University of Ulsan College of Medicine
Seoul, Korea
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Neurological symptoms of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning can manifest not only immediately but also as late as 2 to 6 weeks after successful initial resuscitation as delayed neurological sequelae (DNS). To date, no reliable methods of assessing the probability of DNS after acute CO poisoning have been developed, which make it difficult to research the pathophysiology of DNS and targeting prevention.
(more…)
Won Young Kim, MD PhD
Department of Emergency Medicine
Asan Medical Center
University of Ulsan College of Medicine
Seoul, Korea
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Neurological symptoms of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning can manifest not only immediately but also as late as 2 to 6 weeks after successful initial resuscitation as delayed neurological sequelae (DNS). To date, no reliable methods of assessing the probability of DNS after acute CO poisoning have been developed, which make it difficult to research the pathophysiology of DNS and targeting prevention.
(more…)