Pairing RNA with DNA Genetic Testing Improves Risk Assessment for Hereditary Cancers
 Rachid Karam, MD PhD
Director, Ambry Translational Genomics Lab
Ambry Genetics
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Standard DNA testing for hereditary cancer risk excludes large portions of DNA, thereby missing some mutations. In addition, DNA testing can produce inconclusive results and fail to determine that an error in our DNA increases cancer risk. These limitations impact patients and their families because doctors may not have the information needed to recommend appropriate preventive, early detection, or therapeutic steps. Additionally, relatives may not be referred for genetic testing and obtain the care they would otherwise have gotten if they had learned they had mutations. The study looked at how the addition of RNA genetic testing to standard DNA testing for hereditary cancer risk was able to increase diagnostic yield.
The study looked at the first 2,500 patients that received Ambry Genetics +RNAinsight™, paired RNA and DNA genetic testing for hereditary cancer risk. The data from this study showed that the addition of RNA genetic testing to DNA testing (1) identified new mutations that would have been missed with DNA testing alone, and (2) clarified inconclusive results as disease-causing. (more…)
Rachid Karam, MD PhD
Director, Ambry Translational Genomics Lab
Ambry Genetics
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Standard DNA testing for hereditary cancer risk excludes large portions of DNA, thereby missing some mutations. In addition, DNA testing can produce inconclusive results and fail to determine that an error in our DNA increases cancer risk. These limitations impact patients and their families because doctors may not have the information needed to recommend appropriate preventive, early detection, or therapeutic steps. Additionally, relatives may not be referred for genetic testing and obtain the care they would otherwise have gotten if they had learned they had mutations. The study looked at how the addition of RNA genetic testing to standard DNA testing for hereditary cancer risk was able to increase diagnostic yield.
The study looked at the first 2,500 patients that received Ambry Genetics +RNAinsight™, paired RNA and DNA genetic testing for hereditary cancer risk. The data from this study showed that the addition of RNA genetic testing to DNA testing (1) identified new mutations that would have been missed with DNA testing alone, and (2) clarified inconclusive results as disease-causing. (more…)Association Between Polygenic Risk Score and Risk of Myopia
 Professor Jeremy A. Guggenheim
School of Optometry & Vision Sciences
Cardiff University, UK
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Near-sightedness (myopia) usually develops during childhood and necessitates the use of glasses or contact lenses to correct blurry distance vision. It is also a risk factor for sight-threatening disorders such as glaucoma, retinal detachment and macular degeneration. Promising treatments designed to slow the progression of myopia are becoming available. Building on previous research suggesting that some individuals are genetically predisposed to near-sightedness, we investigated whether a genetic test could identify children at risk of developing myopia. (more…)
Professor Jeremy A. Guggenheim
School of Optometry & Vision Sciences
Cardiff University, UK
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Near-sightedness (myopia) usually develops during childhood and necessitates the use of glasses or contact lenses to correct blurry distance vision. It is also a risk factor for sight-threatening disorders such as glaucoma, retinal detachment and macular degeneration. Promising treatments designed to slow the progression of myopia are becoming available. Building on previous research suggesting that some individuals are genetically predisposed to near-sightedness, we investigated whether a genetic test could identify children at risk of developing myopia. (more…)Hunt For Cause of New Genetic Brain Disorder in Young Children
Disruption of Intestinal Clock Genes May Be Associated with Obesity and Inflammatory Disorders
Study Finds Multigene Testing For All Women With Breast Cancer Can Save Lives and Money
Most BRCA Testing Done in Women Already Diagnosed With Breast Cancer
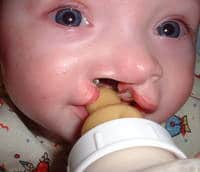
Mechanism Underlying Cleft Lip & Palate Identified in Mouse Model
Genetic Variants Linked To Schizophrenia Also Raise Risk of Other Mental Health Disorders
Precision Medicine: Genetic Variants Predict Response of Eosinophilic Esophagitis to PPIs
Epigenetic Changes Linked to Hypersexual Disorder and Addictive Behaviors
Does PCSK9 Genetic Variation Help Predict Risk of Sepsis?
Left Handedness: Genetic Variants Affect Brain Structure and Function
 Prof. Dominic Furniss, DM MA MBBCh FRCS
Nuffield Department of Orthopaedics, Rheumatology,
and Musculoskeletal Science
University of Oxford
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
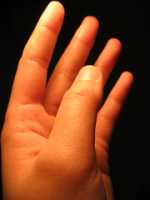
Response: We knew that there was a genetic component to handedness. Twin studies estimated that around 25% of the variation in handedness seen in the human population is down to genetic factors. Genetic factors associated with left handedness had been shown in specific patient populations, but this study has found factors in the general population and correlated them with functional brain imaging to shed more light on this fascinating subject.
We have used both genetic and imaging data from the UK Biobank study to discover genetic variants that are related to left handedness. We have correlated these variants with changes in brain imaging, in particular showing increased functional connectivity between the language processing areas of the brain in left handers. The genetic variants that are associated with left handedness are also near to genes involved in forming the internal skeleton of neurons, and important in brain development, suggesting that being left handed is in part caused by a difference in brain development. It is clear, however, that there are also many non-genetic influences on whether a person is left handed or not. In addition, we confirmed previous observations that being left handed is associated with other neurological problems, such as schizophrenia, and protective of others, such as Parkinson's disease, and showed that this is related to shared genetic factors, and likely reflects differences in brain development. (more…)
Prof. Dominic Furniss, DM MA MBBCh FRCS
Nuffield Department of Orthopaedics, Rheumatology,
and Musculoskeletal Science
University of Oxford
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We knew that there was a genetic component to handedness. Twin studies estimated that around 25% of the variation in handedness seen in the human population is down to genetic factors. Genetic factors associated with left handedness had been shown in specific patient populations, but this study has found factors in the general population and correlated them with functional brain imaging to shed more light on this fascinating subject.
We have used both genetic and imaging data from the UK Biobank study to discover genetic variants that are related to left handedness. We have correlated these variants with changes in brain imaging, in particular showing increased functional connectivity between the language processing areas of the brain in left handers. The genetic variants that are associated with left handedness are also near to genes involved in forming the internal skeleton of neurons, and important in brain development, suggesting that being left handed is in part caused by a difference in brain development. It is clear, however, that there are also many non-genetic influences on whether a person is left handed or not. In addition, we confirmed previous observations that being left handed is associated with other neurological problems, such as schizophrenia, and protective of others, such as Parkinson's disease, and showed that this is related to shared genetic factors, and likely reflects differences in brain development. (more…)USPSTF Issues Genetic Testing Recommendations for BRCA-Related Cancers
Patients Genetically Predisposed to Alzheimer’s Have Difficulty Accessing Memories
Genetic Vulnerability to Early Life Stress Contributes to Risky Drinking and Drug Use in Adolescence
Association Between Aspirin and Mortality From Breast Cancer Depends on Patient’s Genetic Profile
Genetics Plays A Key Role in Where Moles Develop on Skin
High Gluten Diet Adds to Risk of Celiac Disease in Genetically Predisposed Children
This study adds another piece to the celiac puzzle, i.e. what main risk factors are involved in the devolpment of...
Payer Coverage for Genetic Testing of Cardiovascular Genes Varies by Insurer
 Nancy Niguidula, MS, DPH
Doctorate in Public Health in Toxicology
Ambry Genetics
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The clinical presentations of many inherited cardiovascular conditions overlap; thus, genetic testing may clarify diagnoses, help with risk stratification, facilitate appropriate clinical management decisions, and aid in identifying asymptomatic, at-risk relatives. A large number of professional societies have developed practice guidelines and recommendations for genetic testing of cardiovascular diseases. These include international and collaborative expert panels that establish genetic screening and treatment recommendations by drawing on evidence-based medicine. To further strengthen the clinical utility of cardiovascular genetic testing, the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) published a guideline for 59 genes with clinical actionability that should be reported if found on whole exome sequencing, even when unrelated to the testing indication.
(more…)
Nancy Niguidula, MS, DPH
Doctorate in Public Health in Toxicology
Ambry Genetics
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The clinical presentations of many inherited cardiovascular conditions overlap; thus, genetic testing may clarify diagnoses, help with risk stratification, facilitate appropriate clinical management decisions, and aid in identifying asymptomatic, at-risk relatives. A large number of professional societies have developed practice guidelines and recommendations for genetic testing of cardiovascular diseases. These include international and collaborative expert panels that establish genetic screening and treatment recommendations by drawing on evidence-based medicine. To further strengthen the clinical utility of cardiovascular genetic testing, the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) published a guideline for 59 genes with clinical actionability that should be reported if found on whole exome sequencing, even when unrelated to the testing indication.
(more…)Alzheimer’s: Genetic Variants Mediate Effects of Poor Diet in Cognitive Decline
Genetic Variants Linked to Life-threatening Cardiac Arrhythmias in Patients With Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Implanted Defibrillators
Americans Support Gene Therapies Even If They Cost More

MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Wayne Winegarden, Ph.D.
Director, Center for Medical Economics and Innovation
Pacific Research Institute
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this poll? Would you tell us a little about the Center for Medical Economics and Innovation?
Response: Recent press reports have focused on how extensive innovative gene therapies can be. PRI was interested in learning where Americans stand on these cures of the future, and commission a new national opinion survey to find out.
The Center for Medical Economics and Innovation is a new center launched by PRI this spring to research and advance policies showing how a thriving biomedical and pharmaceutical sector benefits both patients and economic growth. Medical innovation is an important driver of economic growth, responsible for over $1.3 trillion in economic activity each year. As the Milken Institute has found, every job in the biomedical sphere supports another 3.3 jobs elsewhere in the economy.
Among the activities of the Center – which can be accessed at www.medecon.org – are providing free-market analysis to evaluate current policy proposals, producing easy-to-understand data and analysis on current trends in medical science, breaking down complex issues like pharmaceutical and biomedical pricing structures, and demonstrating the benefits that market-based reforms can offer patients and the U.S. health care system. (more…)
Children with Birth and Chromosomal Defects More Likely to Develop Cancer
World Trade Center 9/11 Dust: Altered Gene Expression Links Exposure to Prostate Cancer Risk
Metagenomic Sequencing Enhanced Diagnosis of Meningitis and Encephalitis Infections
Does Genetic Information Encourage Doctors to Switch Anticoagulation Medications?
Why Do Some People Get a Dog?
 Tove Fall PhD
Senior author of the study
Associate Professor in Epidemiology
Department of Medical Sciences and the Science for Life Laboratory
Uppsala University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Dog ownership is common in the Western society but little is known about what actually makes people get a dog.
We conducted a twin study to understand whether the genetic make-up has an influence on this choice. We found that more than 50% of the differences in dog ownership is explained by genetic variants. (more…)
Tove Fall PhD
Senior author of the study
Associate Professor in Epidemiology
Department of Medical Sciences and the Science for Life Laboratory
Uppsala University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Dog ownership is common in the Western society but little is known about what actually makes people get a dog.
We conducted a twin study to understand whether the genetic make-up has an influence on this choice. We found that more than 50% of the differences in dog ownership is explained by genetic variants. (more…)Genes Determine Why We Don’t All Smell the Same
Machine Learning Can Analyze Entire Transcriptome To Improve Diagnosis of Difficult Cancers
 Jasleen Grewal, BSc.
Genome Sciences Centre
British Columbia Cancer Research Centre
Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Cancer diagnosis requires manual analysis of tissue appearance, histology, and protein expression. However, there are certain types of cancers, known as cancers of unknown primary, that are difficult to diagnose based purely on their appearance and a small set of proteins. In our precision medicine oncogenomics program, we needed an accurate approach to confirm diagnosis of biopsied samples and determine candidate tumour types for where the primary site of the cancer was uncertain. We developed a machine learning approach, trained on the gene expression data of over 10,688 individual tumours and healthy tissues, that has been able to achieve this task with high accuracy.
Genome sequencing offers a high-resolution view of the biological landscape of cancers. RNA-Seq in particular quantifies how much each gene is expressed in a given sample. In this study, we used the entire transcriptome, spanning 17,688 genes in the human genome, to train a machine learning method for cancer diagnosis. The resultant method, SCOPE, takes in the entire transcriptome and outputs an interpretable confidence score from across a set of 40 different cancer types and 26 healthy tissues. (more…)
Jasleen Grewal, BSc.
Genome Sciences Centre
British Columbia Cancer Research Centre
Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Cancer diagnosis requires manual analysis of tissue appearance, histology, and protein expression. However, there are certain types of cancers, known as cancers of unknown primary, that are difficult to diagnose based purely on their appearance and a small set of proteins. In our precision medicine oncogenomics program, we needed an accurate approach to confirm diagnosis of biopsied samples and determine candidate tumour types for where the primary site of the cancer was uncertain. We developed a machine learning approach, trained on the gene expression data of over 10,688 individual tumours and healthy tissues, that has been able to achieve this task with high accuracy.
Genome sequencing offers a high-resolution view of the biological landscape of cancers. RNA-Seq in particular quantifies how much each gene is expressed in a given sample. In this study, we used the entire transcriptome, spanning 17,688 genes in the human genome, to train a machine learning method for cancer diagnosis. The resultant method, SCOPE, takes in the entire transcriptome and outputs an interpretable confidence score from across a set of 40 different cancer types and 26 healthy tissues. (more…)