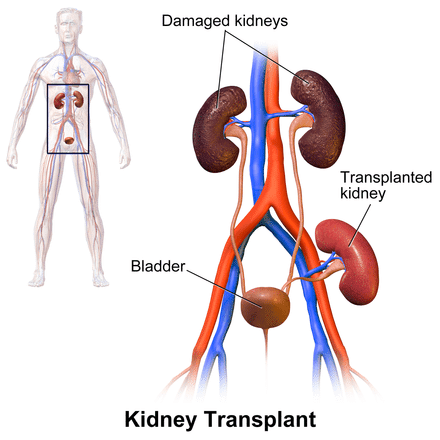
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Michael Liu, MPhil
Rhodes Scholar,MPhil in Evidence-Based Social Intervention and Policy Evaluation.
Harvard Medical School
Boston, Massachusetts
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Over the past few decades, research has shown that lesbian, gay, and bisexual (LGB) individuals have worse health outcomes and face unique challenges related to their experiences and costs of care. These disparities are driven by “minority stress” associated with belonging to a marginalized group. Such stressors erode health through a range of structural and interpersonal forces, including employment discrimination, family rejection, and internalized stigma
One early analysis established national baseline estimates for LGB health outcomes using 2013-2014 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) data. Since then, there have been substantial shifts in social policy and public opinion that may have differentially affected sexual minority subgroups. The US Supreme Court decision in
Obergefell v. Hodges guaranteed the constitutional right to same-sex marriage across all states. Over the last decade, states have expanded rights and protections for LGB populations related to employment and housing discrimination, sexual orientation conversion efforts, HIV criminalization, and religious exemptions. Public support for LGB-related issues has also been increasing with more representation in media, uptake of LGB-affirming policies, and advocacy efforts.
No studies have assessed national trends in health status or healthcare access among specific sexual minority subgroups amid the rapidly shifting sociocultural and policy landscape. Thus, we sought out to evaluate if and how health status and healthcare access have changed between 2013 and 2018 in the US among LGB adults, and whether differences relative to their heterosexual counterparts have changed over time.
(more…)