Author Interviews, Cancer Research, Nutrition, Supplements / 06.01.2022
Mistaken Beliefs About Supplements and Vitamins Among Cancer Patients
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr Rana Conway PhD RNutr
Research Fellow
Energy Balance & Cancer Group, and Obesity Research Group
Research Department of Behavioural Science and Health
University College London
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We’ve seen great advances in cancer diagnosis and treatment in recent years which means the number of people living with and beyond a cancer diagnosis is rapidly increasing. The WCRF and CRUK recommend improving diet and exercise to reduce the risks of cancer coming back but we know anecdotally that supplements are sometimes seen as an easier option, and people who’ve had cancer are often interested to know if they should be taking any supplements. (more…)


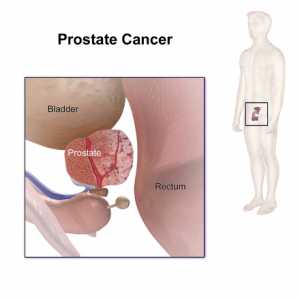
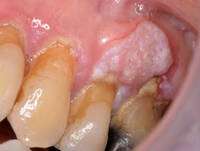










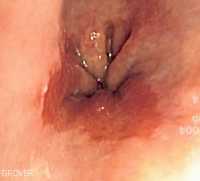


 MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Eleonora Leucci, Ph.D Assistant Professor
Laboratory for RNA Cancer Biology
Department of Oncology
KU Leuven
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Back in 2016, while I was characterising the RNA SAMMSON as essential for mitochondrial translation in melanoma, I noticed that its inhibition was causing cell death across a large spectrum of melanoma cell lines and models, irrespectively of their genetic background and cell state. At that time I still did not know why the effect was so pronounced on melanoma cells, but I knew that antibiotics of the tetracycline family could also block mitochondrial translation and I thought about repurposing them to treat melanoma.
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Eleonora Leucci, Ph.D Assistant Professor
Laboratory for RNA Cancer Biology
Department of Oncology
KU Leuven
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Back in 2016, while I was characterising the RNA SAMMSON as essential for mitochondrial translation in melanoma, I noticed that its inhibition was causing cell death across a large spectrum of melanoma cell lines and models, irrespectively of their genetic background and cell state. At that time I still did not know why the effect was so pronounced on melanoma cells, but I knew that antibiotics of the tetracycline family could also block mitochondrial translation and I thought about repurposing them to treat melanoma.
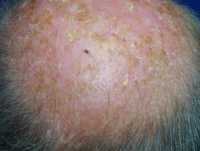






 Professor Marie-Aleth Richard
EADV Communications Committee Chair
Professor, University Hospital of La Timone
Marseille, France
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this Roundtable event? Would you describe the mission of the European Commission’s Beating Cancer Plan?
Response: Europe’s Beating Cancer Plan is the first, comprehensive EU strategy on cancer, aimed at tackling the disease through all key stages: prevention; early detection; diagnosis and treatment; and quality of life of cancer patients and survivors. The Plan also aims to create opportunities to improve cancer care through research and innovative projects, such as artificial intelligence, and to promote equal access to knowledge and treatments in cancer care across Europe.
The EADV seeks to create a bridge between the EU health policy agenda and scientific research, by engaging with policymakers, patient organisations and other stakeholders to support a patient centric-approach; tackling melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC) at all stages of the pathway, from prevention to follow-up care.
Through our Roundtable event, the EADV brought together these key stakeholders to evaluate the effectiveness of the EBCP on preventing both melanoma and NMSC, as well as identify joint recommendations that step-up measures towards this goal.
Professor Marie-Aleth Richard
EADV Communications Committee Chair
Professor, University Hospital of La Timone
Marseille, France
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this Roundtable event? Would you describe the mission of the European Commission’s Beating Cancer Plan?
Response: Europe’s Beating Cancer Plan is the first, comprehensive EU strategy on cancer, aimed at tackling the disease through all key stages: prevention; early detection; diagnosis and treatment; and quality of life of cancer patients and survivors. The Plan also aims to create opportunities to improve cancer care through research and innovative projects, such as artificial intelligence, and to promote equal access to knowledge and treatments in cancer care across Europe.
The EADV seeks to create a bridge between the EU health policy agenda and scientific research, by engaging with policymakers, patient organisations and other stakeholders to support a patient centric-approach; tackling melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC) at all stages of the pathway, from prevention to follow-up care.
Through our Roundtable event, the EADV brought together these key stakeholders to evaluate the effectiveness of the EBCP on preventing both melanoma and NMSC, as well as identify joint recommendations that step-up measures towards this goal. 



