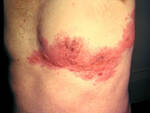
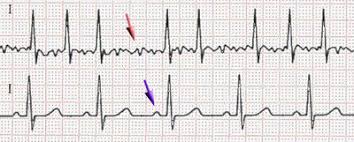
U Michigan Study Finds Biomarkers Can Predict Myocarditis from Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Multiple Demographic Disparities in Cardiovascular Risk After Pediatric and Youth Cancer
Personalized Micronutrients May Benefit Cardiovascular Health
Herpes Zoster: Persistent Increased Risk of Cardiac Event or Stroke After Shingles
Wearables to Detect Heart Disease: Patients Most at Risk Less Likely to Use them
Study Finds Reduced Kidney Disease Progression with DOACs vs Vitamin K Antagonists
USPSTF Evaluates Statin Use for Primary Prevention of Heart Disease
NEJM: Study Compares PCI to Medical Therapy to Reduce Death or Hospitalization from Heart Failure
Increased Adrenal Hormone Aldosterone Linked to Greater Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease
USPSTF: Evaluates Benefits of Diet and Exercise Counseling for Adults Without Known Heart Disease Risk Factors
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lori Pbert, Ph.D Professor, Department of Population and Quantitative Health Sciences Associate chief of the Division of Preventive and Behavioral Medicine Founder and director of the Center for Tobacco Treatment Research and Training University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School Dr. Pbert joined the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in January 2019
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Heart attacks and strokes are the number one killer of adults in the United States. Based on the evidence we reviewed, the Task Force found that some people would benefit from counseling interventions to support their cardiovascular health, however the overall benefits are small. For that reason, we continue to recommend that healthcare professionals decide together with their patients who do not have cardiovascular disease risk factors whether counseling interventions on healthy diet and physical activity might help them prevent heart attacks and strokes. This is a C grade recommendation. (more…)
Premature Menopause May Increase Risk of Heart Failure and AFib
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Jean Shin Department of Family Medicine Korea University College of Medicine Seoul,Republic of Korea
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Younger age at menopause is a possible risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. However, data on the association among premature menopause, age at menopause, and the risk of heart failure and atrial fibrillation are lacking. We aimed to examine the association of premature menopause and age at menopause with the risk of heart failure and atrial fibrillation. (more…)
Precision Genetics Can Identify Specific Causes of Heart Failure
Not All Patients with Heart Failure Benefit from Salt Restriction
USPSTF: Task Force Recommends Against Beta Carotene and Vitamin E to Prevent Heart Disease or Cancer
First-Line Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Cardiovascular Outcomes of SGLT-2 Inhibitors vs Metformin
- Cardiovascular disease affects approximately one-third of the population with type 2 diabetes and accounts for 50%–80% of their mortality
- 1 in 10 people in the US has diabetes