MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr Dilip Kachhawa, MD
Department of Skin & Venereal Disease
Dr Sampurnanand Medical College
Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
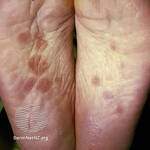
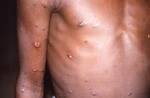
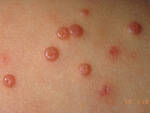
Response: Molluscum Contagiosum (MC) is an infection caused by molluscipoxvirus. It is difficult to study since the virus only survives in human skin, and therefore there isn’t an animal or cell model to study potential treatments. Molluscum lesions appear as raised, domed shaped skin-colored lesions and can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the face, neck, arms, legs, and abdomen. Sometimes there are few lesions, but clusters of several lesions can appear. Children are the most likely to get molluscum, and the virus is highly contagious, transmitted by direct contact with infected skin or contaminated objects, like towels, linens and toys. Scratching can cause autoinoculation which is when a person reinfects themself.
MC is very common, impacting an estimated 6 million adults and mostly children in the US each year. In 2010, there was an estimated 122 million cases worldwide. It occurs primarily in humid and warm climates, and transmission via swimming pools and bathtubs may be possible. Therefore, molluscum is often called “water warts.”
Many physicians may take a “watch and wait” approach since the virus may clear on its own. However, it can take months to up to 5 years for some to experience complete clearance, In the meantime, the person is still highly contagious and may spread the virus to others, particularly children. Lesions can be bothersome, causing itching and sometimes a secondary infection. There is also a psychosocial component. In a recent study, 1 in 10 children with molluscum experienced a major quality of life issue.
Berdazimer Gel, 10.3% is a potential first-in-class topical controlled-nitric oxide releasing medication containing Berdazimer (sodium), a new chemical entity, and the active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3%. The mechanism of action of berdazimer in the treatment of molluscum is unknown, but in vitro lab studies show that the nitric oxide, released when berdazimer is combined with a hydrogel, may impede viral replication and perhaps help body’s natural immune response against molluscum.
(more…)












 Sean M Hughes MA
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
University of Washington
Seattle, WA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Young women are at elevated risk of getting sexually transmitted infections at the age when they typically start to have sexual intercourse. It’s not known whether this elevated risk is a consequence of behavioral factors (such as choices around use of barrier protection), physiological factors (such as a difference in the immune system) or a combination of both. In this study, we investigated a physiological factor: the immune system in the vagina.
Sean M Hughes MA
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
University of Washington
Seattle, WA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Young women are at elevated risk of getting sexually transmitted infections at the age when they typically start to have sexual intercourse. It’s not known whether this elevated risk is a consequence of behavioral factors (such as choices around use of barrier protection), physiological factors (such as a difference in the immune system) or a combination of both. In this study, we investigated a physiological factor: the immune system in the vagina.