Author Interviews, Heart Disease, JAMA, Surgical Research / 16.06.2019
TAVR vs Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Among Low-Risk Patients With Aortic Stenosis
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Fausto Biancari, MD, PhD
Professor
University of Turku and University
Oulu, Finland
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
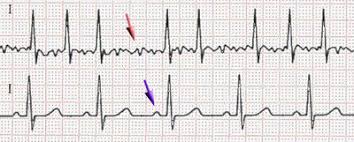
Response: Current data is scarce regarding the short- and midterm benefit of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) compared to surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) in low-risk patients with severe aortic valve stenosis.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: In this observational study on 2841 low-risk patients with aortic valve stenosis from the Finnish nationwide FinnValve registry, propensity score matching analysis showed similar 30-day and three-year survival after TAVR and SAVR.
(more…)