Author Interviews, Cancer Research, JAMA, Lung Cancer, NIH, Race/Ethnic Diversity, Stanford / 01.11.2023
Lung Cancer: Stanford Risk-Based Model Reduces Screening Disparities
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Summer S Han, PhD
Associate Professor
Quantitative Sciences Unit
Stanford Center for Biomedical Informatics Research (BMIR)
Department of Neurosurgery and Department of Medicine
Department of Epidemiology & Population Health (by Courtesy)
Stanford University School of Medicine
Dr. Eunji Choi PhD
Instructor, Neurosurgery
Department: Adult Neurosurgery
Stanford University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
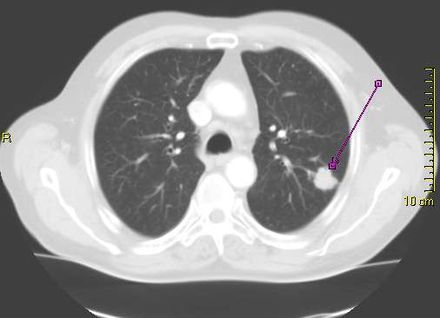
- Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States, killing about 127,000 people annually, but it can be treatable if detected early.
- Low-dose computed tomography, or CT scan, has been shown to significantly reduce the number of lung cancer deaths. But because the radiation delivered by the scans can be harmful (they use on average about 10 times the radiation of standard X-rays), only those people at relatively high risk for lung cancer should be screened. The two biggest risk factors for lung cancer are exposure to tobacco smoke and age. Current national guidelines that rely on age and smoking exposure to recommend people for lung cancer screening are disproportionally failing minority populations including African Americans, according to a new study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine.
- In 2021, the national guidelines by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) issued revised recommendation guidelines on lung cancer screening, lowering the start age from 55-year to 50-year and the smoking pack-year criterion from 30 to 20, compared to the 2013 USPSTF criteria. In comparison to the 2013 criteria, the new modifications have been shown to lessen racial disparities in screening eligibility between African Americans and Whites. However, potential disparities across other major racial groups in the U.S., such as Latinos, remains poorly examined.
- Meanwhile, risk prediction model assesses a person’s risk score of developing an illness, such as lung cancer.