Author Interviews, Dermatology, Surgical Research / 05.03.2019
Lipomas: Deoxycholic Acid (Kybella®) Can Shrink Tumors Before Removal
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Hooman Khorasani, M.D.
Cosmetic Surgeon & Mohs Skin Cancer Surgeon
Icahn School of Medicine at Mt. Sinai
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
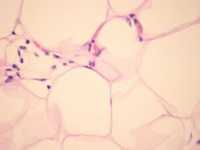
Response: Lipomas are tumors composed of mature fat cells located just beneath the skin surface. They are the most common soft tissue tumor and are estimated to occur in 1% of the population. These benign tumors are more common in overweight individuals, diabetics, patients with elevated serum cholesterol, and those suffering from familial multiple lipomatosis. Most of these tumors are treated for cosmetic reasons; however, large lipomas can also cause significant functional impairment. Traditional treatment includes surgical removal and / or liposuction.
Deoxycholic acid is a member of the bile acid family that assists in the breakdown of fat. We investigated the use of deoxycholic acid injections to reduce the size of large lipomas prior to surgical removal.
(more…)


























 Dr Paul Gentil
Faculty of Physical Education and Dance
Federal University of Goias
Goiania, Brazil
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Although being overweight and/or obese are associated with numerous health risks, the prevalence of both are continuing to increase worldwide. The treatment would include anything that results in an increase in energy expenditure (exercise) or a decrease in energy intake (diet). However, our metabolism seems to adapt to variations in physical activity to maintain total energy expenditure. Although lower-than-expected weight loss is often attributed to incomplete adherence to prescribed interventions, there are other factors that might influence the results, such as, metabolic downregulation.
So, instead of making people spend more calories, maybe we have to think on how to promote metabolic changes in order to overcome these physiological adaptations above-mentioned. In this regard, high intensity training might be particularly interesting as a strategy to promote fat loss. Irrespective the amount of calories spent during training, higher intensity exercise seems to promote many physiological changes that might favor long-term weight loss. For example, previous studies have shown that interval training is able to promote upregulation of important enzymes associated with glycolysis and beta oxidation pathways, which occurs in a greater extent than with moderate intensity continuous exercise.
Our findings suggest that interval training might be an important tool to promote weigh loss. However, I t might be performed adequately and under direct supervision in order to get better results.
Dr Paul Gentil
Faculty of Physical Education and Dance
Federal University of Goias
Goiania, Brazil
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Although being overweight and/or obese are associated with numerous health risks, the prevalence of both are continuing to increase worldwide. The treatment would include anything that results in an increase in energy expenditure (exercise) or a decrease in energy intake (diet). However, our metabolism seems to adapt to variations in physical activity to maintain total energy expenditure. Although lower-than-expected weight loss is often attributed to incomplete adherence to prescribed interventions, there are other factors that might influence the results, such as, metabolic downregulation.
So, instead of making people spend more calories, maybe we have to think on how to promote metabolic changes in order to overcome these physiological adaptations above-mentioned. In this regard, high intensity training might be particularly interesting as a strategy to promote fat loss. Irrespective the amount of calories spent during training, higher intensity exercise seems to promote many physiological changes that might favor long-term weight loss. For example, previous studies have shown that interval training is able to promote upregulation of important enzymes associated with glycolysis and beta oxidation pathways, which occurs in a greater extent than with moderate intensity continuous exercise.
Our findings suggest that interval training might be an important tool to promote weigh loss. However, I t might be performed adequately and under direct supervision in order to get better results.

