Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Cognitive Issues, Exercise - Fitness / 23.04.2022
Long-Term Health Outcomes Associated with College Football
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Robert A. Stern, Ph.D.
Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Anatomy & Neurobiology
Director of Clinical Research, BU CTE Center
Senior Investigator, BU Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center
Boston University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The link between playing American football at the professional level and later-life brain disorders like chronic traumatic encephalopathy – or CTE -- and ALS has received increasing attention over the past 15 years. Previous research has shown that former NFL players are more likely to die from CTE and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and more likely to report cognitive impairment, behavioral changes, and dementia during life. Despite previous research focusing on the later-life effects of playing American football at the professional level, the long-term effects of college football participation remain largely unknown.
We had two goals for this new investigation. The first was to conduct a survey of the current overall health status, including cognitive and other neurological disorders, of older former college American football players compared with men in the general population. The second goal was to examine the mortality rate and causes of death in a cohort of older former college football players. The target population for this study was all 447 former Notre Dame football players who were listed as seniors on the varsity rosters during the 1964-1980 seasons. This was the era of legendary coaches Ara Parseghian and Dan Devine. I should add that this study was fully independent of the University of Notre Dame.
(more…)








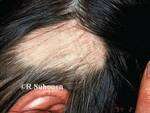
 Brett King, MD, PhD, FAAD
Associate Professor of Dermatology
Yale School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder marked by disfiguring, non-scarring hair loss, and there are no therapies approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of the disease. JAK inhibitors are showing promise for treatment of severe alopecia areata. In this work, the pooled results of two phase 3 clinical trials of the JAK inhibitor baricitinib were reported out to 52 weeks.
Brett King, MD, PhD, FAAD
Associate Professor of Dermatology
Yale School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder marked by disfiguring, non-scarring hair loss, and there are no therapies approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of the disease. JAK inhibitors are showing promise for treatment of severe alopecia areata. In this work, the pooled results of two phase 3 clinical trials of the JAK inhibitor baricitinib were reported out to 52 weeks.






 Response: Cigarette smoking is one of the well-established causes of periodontitis, but the effect of using electronic cigarettes (e-cig), especially its long-term impact on periodontal health, is not yet clearly understood. Considering the increased popularity of e-cig use, especially among teenagers and young adults, and the known effect of high nicotine concentration in e-cigarette products, we conducted this clinical research to see if there were differences in periodontal health between e-cig users, traditional smokers, and nonsmokers. The study consisted of two visits, 6 months apart, where measures of oral and periodontal health were obtained.
Our data showed significantly greater clinical attachment loss in the e-cigarette users and cigarette smokers than in the non-smokers at both study visits. In only e-cigarette users, we observed an over 0.2 mm average increase in the clinical attachment loss after 6 months.
Response: Cigarette smoking is one of the well-established causes of periodontitis, but the effect of using electronic cigarettes (e-cig), especially its long-term impact on periodontal health, is not yet clearly understood. Considering the increased popularity of e-cig use, especially among teenagers and young adults, and the known effect of high nicotine concentration in e-cigarette products, we conducted this clinical research to see if there were differences in periodontal health between e-cig users, traditional smokers, and nonsmokers. The study consisted of two visits, 6 months apart, where measures of oral and periodontal health were obtained.
Our data showed significantly greater clinical attachment loss in the e-cigarette users and cigarette smokers than in the non-smokers at both study visits. In only e-cigarette users, we observed an over 0.2 mm average increase in the clinical attachment loss after 6 months.