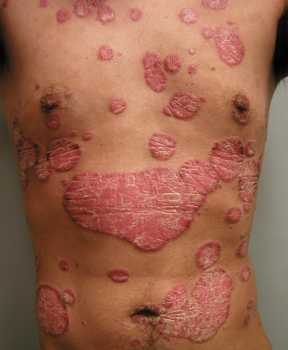
Author Interviews, Diabetes, NEJM / 09.02.2023
NEJM: New Oral Medication Addresses Common Itchy Back Condition
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Brian S Kim, MD, MTR
Sol and Clara Kest Professor
Vice Chair of Research | Site Chair, Mount Sinai West and Morningside
Director, Mark Lebwohl Center for Neuroinflammation and Sensation
The Kimberly and Eric J. Waldman Department of Dermatology
Precision Immunology Institute | Friedman Brain Institute
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We generated preliminary data in mice that difelikefalin suppresses itch robustly with very little to no effect on inflammation in a model of atopic dermatitis. This led us to hypothesize that the primary mode of action of difelikefalin must be by direct modulation of sensory neurons to suppress itch and thus would be best suited for a neuropathic itch condition. These are conditions in which itch occurs relatively independently of skin inflammation as in atopic dermatitis due to hyperactive nerves.
(more…)





 Tom Arild Torstensen
Department of Neurobiology, Care Sciences and Society
Division of Physiotherapy,
Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, Sweden and
Holten Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: People suffering from pain due to knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a major and increasing problem. There there is today good scientific evidence for different forms of exercise therapy, but there is no agreement regarding what type of exercises and what dose of exercise therapy is best. Thus, we wanted to investigate if high dose medical exercise therapy is superior to low dose.
Tom Arild Torstensen
Department of Neurobiology, Care Sciences and Society
Division of Physiotherapy,
Karolinska Institutet, Huddinge, Sweden and
Holten Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: People suffering from pain due to knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a major and increasing problem. There there is today good scientific evidence for different forms of exercise therapy, but there is no agreement regarding what type of exercises and what dose of exercise therapy is best. Thus, we wanted to investigate if high dose medical exercise therapy is superior to low dose.













 Alden Mileto, BA
Department of Medical Education
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Scranton, PA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The drug buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, originally developed in the 1960s as an alternative to the stronger full opioid mu receptor agonists like morphine. Today, the drug is sometimes used for pain, but is more often used as a treatment for Opioid Use Disorder (OUD). Since the 2002 federal approval for buprenorphine use in treatment of OUD, there has been an increase in buprenorphine prescription across all states.
However recent studies have showed a disproportionate increase in buprenorphine prescriptions to rural/ less populated areas in comparison to urban/densely populated areas. The objective of this study [1] was to analyze the trends in buprenorphine distribution, overall and by three-digit zip codes, in Pennsylvania from 2010-2020.
Alden Mileto, BA
Department of Medical Education
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Scranton, PA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The drug buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist, originally developed in the 1960s as an alternative to the stronger full opioid mu receptor agonists like morphine. Today, the drug is sometimes used for pain, but is more often used as a treatment for Opioid Use Disorder (OUD). Since the 2002 federal approval for buprenorphine use in treatment of OUD, there has been an increase in buprenorphine prescription across all states.
However recent studies have showed a disproportionate increase in buprenorphine prescriptions to rural/ less populated areas in comparison to urban/densely populated areas. The objective of this study [1] was to analyze the trends in buprenorphine distribution, overall and by three-digit zip codes, in Pennsylvania from 2010-2020.