Author Interviews, Cancer Research, Dermatology, JAMA / 11.12.2019
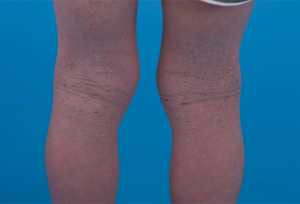
Atopic Dermatitis Linked to Skin and Kidney Cancer
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lily Wang
Student at University of Toronto
Toronto, Ontario, Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Impaired skin barrier and aberrant immune function in atopic dermatitis (AD) may impact immune response to malignancy. Conflicting data exist on the risk of cancer in patients with AD. The purpose of our study was to determine the risk of non-cutaneous and cutaneous cancers in patients with atopic dermatitis compared to the general population (i.e. without AD). (more…)