MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Ben Gold, a PhD candidate
Lab of Robert Zatorre
The Neuro (Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital)
McGill University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Music is just sound in air, but it carries considerable power. It captivates our brain’s reward system, we devote an enormous amount of time and money to it, and we're just beginning to tap its therapeutic potential. We wanted to explore how something so abstract could have such an impact, and since music is so well suited to establishing and manipulating patterns of sound as it unfolds, we focused on how it manipulates expectations.
Previous research has shown that surprises are often the most emotional and pleasurable moments in music listening, but whether and how this engaged the brain's reward system was unclear. So we adapted an experimental protocol designed for studying learning and surprise about more concrete rewards like food or money, and applied it to a musical context during brain imaging. This protocol relies on participants making decisions from which we could infer their expectations, allowing us to estimate how surprised they were by each outcome whenever it occurred. In our case, we asked participants to make choices about colors and directions that were associated with different musical outcomes, but we didn't tell them what those associations were so that they they started with no expectations and learned as they went.
We found that our participants could learn about music just like they would learn about how to find food or win money, and that the same neural process was involved. Specifically, we saw that the activity of the nucleus accumbens -- a central hub of the reward system -- reflected both how pleasant and how surprising each musical outcome was: a computation known as a reward prediction error. Across individuals, those who better represented these reward prediction errors in their nucleus accumbens also learned better about the music in the experiment, making more decisions over time to find the music they preferred. (more…)
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Sunil A. Sheth, MD
Department of Neurology
McGovern Medical School at UTHealth
Houston, TX 77030
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: There is no country in the world where the absolute number of people living with or died from stroke has declined between 1990 and 2013. In the US, approximately 795,000 people experience a stroke each year with nearly 90% being acute ischemic stroke (AIS), which remains the leading cause of adult disability in the US.
In 2015 landmark clinical trials demonstrated that endovascular stroke treatments (EST) for patients with large vessel occlusion (LVO) leads to dramatic improvements in patient outcomes. However, in the wake of these results, stroke systems of care around the globe are now faced with the daunting task of ensuring that patients with AIS have access to appropriate screening and therapy.
The evidence of benefit for endovascular stroke that emerged from these trials was derived from treatments rendered almost exclusively at high volume stroke centers, with specialized neuro-imaging, neuro-intensive care, neuro-rehabilitation and neuro-nursing. However, since the publication and adoption of these findings into guidelines, it has become well-established that the likelihood of good neurologic outcome for these patients remains dependent on minimizing delays in treatment. Even 15-minute delays in endovascular reperfusion have been associated with quantifiable decrements in clinical outcomes. As such, there has been an increase in demand for the procedure as well as calls for the dissemination of the treatment away from tertiary-care referral centers into the community, to avoid the costly delays associated with inter-hospital transfer (IHT). On the other hand, transferring endovascular stroke patients to higher volume centers has also been associated with reduced mortality. In the absence of clear data on the relative efficacy of EST in lower volume centers, this lack of clarity on the optimal distribution of endovascular stroke resources had led to considerable confusion, with stroke center certifying agencies such as The Joint Commission initially requiring physician and hospital minimal EST volume requirements for certification, and then very recently revoking and then reinstating that criterion.
Given the need to structure stroke systems of care in the modern endovascular stroke era, as well as the poorly characterized effect on EST outcomes away from tertiary-care referral centers, understanding the trends in treatment patterns as well as outcomes in relation to treatment volumes and IHT is of vital importance. The study described here provides for the first time large-scale data on the utilization of the procedure as well as the finding that its outcomes are directly tied to annual volumes.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Cost of Health Care, JAMA, Pharmacology, University of Pittsburgh / 19.02.2019
Price of Existing Biologics Increased When New Drugs Entered Market
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Alvaro San-Juan-Rodriguez, PharmD
Pharmacoeconomics, Outcomes and Pharmacoanalytics Research Fellow
Pharmacy and Therapeutics
School of Pharmacy
University of Pittsburgh
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Before 2009, etanercept (Enbrel®), infliximab (Remicade®), and adalimumab (Humira®) were the only tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors approved by the FDA for rheumatoid arthritis. Subsequently, 3 therapies gained FDA approval: subcutaneous golimumab (Simponi®) in April 2009, certolizumab pegol (Cimzia®) in May 2009, and intravenous golimumab (Simponi Aria®) in July 2013. All 6 agents are brand-name drugs.
Our study aimed to evaluate how the prices of existing TNF inhibitors (Enbrel®, Remicade® and Humira®) changed in response to the market entry of new TNF inhibitors. (more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, OBGYNE / 19.02.2019
Risk of Spontaneous Abortion & Birth Defects with Oral Yeast Drug During Pregnancy
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Anick Bérard PhD FISPE
Research chair FRQS on Medications and Pregnancy
Director, Réseau Québécois de recherche sur le médicament
Professor, Research Chair on Medications, Pregnancy and Lactation
Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Montrealand
Director, Research Unit on Medications and Pregnancy
Research Center
CHU Ste-Justin
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Yeast infections are common during pregnancy (10%). Although topical treatments are first-line therapies, yeast infections during gestation are often more severe and are resistant to topical options. Hence, low dose oral fluconazole is often the treatment of choice for pregnant women (1 dose for 1 day).
Human and animal studies have shown that high dose of fluconazole is teratogenic.Few studies are available for the risk associated with low dose of fluconazole (the most used during pregnancy). Also, no one has studied the combined effect of low- and high-dose fluconazole use during pregnancy on overall adverse pregnancy outcomes (spontaneous abortions, stillbirths and major malformations). (more…)
Author Interviews, Dermatology / 19.02.2019
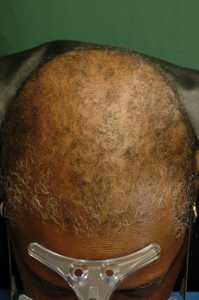
Mutations Linked to Scarring Hair Loss in African American Women Identified
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Eli Sprecher MD PhD
Professor and Chair, Division of Dermatology
Deputy Director General for R&D and Innovation
Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center
Frederick Reiss Chair of Dermatology
Sackler Faculty of Medicine
Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel and
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA) is a form of hair loss (alopecia) which is extremely common and affects one in every 20 women of African origin. It starts usually during the fourth decade of life. Because it can be inherited from mothers to their children, it is thought to have a genetic basis. On the other hand, it is known to mainly affect women who use to groom their hair intensively. Thus it was thought that the disease stems from some form of inherited susceptibility to the damage incurred to the hair follicle by grooming habits.
In the study we published, we searched for the genetic basis of CCCA.
In contrast with the common form of alopecia (androgenetic alopecia or female pattern alopecia), CCCA is associated with scarring of the scalp skin, which means that once hair is lost, it will likely not re-grow.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Personalized Medicine, Weight Research / 19.02.2019
Genes Help Determine Whether You Are Shaped Like an Apple or Pear
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Ruth Loos, PhD
The Charles Bronfman Professor in Personalized Medicine
Director, Genetics of Obesity and Related Traits Program
Co-Director, Charles Bronfman Institute for Personalized Medicine
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
New York, NY
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Which type of body fat distribution carries greater risk of diabetes or other obesity-related health disorders?
Response: Obesity broadly consists of two component; [1] there is overall body size (assessed using BMI) and [2] there is fat distribution (assessed using WHR). Both are “heritable”, which mean that they are in part determined by our genome (and the other part is determined by our lifestyle).
Over the past 15 years, geneticists have used an approach to screen the whole genome of thousands of people to identify genetic variations that differ between e.g. obese people vs non-obese people.
We have applied this approach to both components of obesity and have found so far that genes for “overall body size” seem to act in the brain, likely controlling hunger, satiety, reward, etc., whereas the genes that determine where in the body the excess fat will be stored when you gain weight (i.e. fat distribution) seem to act more “locally” at the fat cell level itself, determining the storage and release of fat. (more…)
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
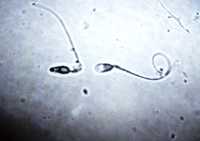
Dr Simone Immler PhD
School of Biological Sciences
University of East Anglia
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Sperm produced by one male vary substantially both in their genetic content as well as their swimming ability including speed and duration. In a previous study in the zebrafish, we showed that sperm swimming duration is at least partly determined by the underlying haploid genetic content carried by the different sperm within an ejaculate (alavioon et al. 2017 PNAS). If sperm with different swimming ability differ in their genetic content, we expect to see differences among the offspring sired by sperm that vary on their swimming ability.
In our new study, we tested how selection on sperm swimming duration affects offspring fitness. We performed in vitro fertilisation assays mimicking natural conditions in the externally fertilising zebrafish. We split the ejaculate of one male into two halves and in one half we added the sperm straight away to the eggs, allowing all motile sperm to have a go at fertilising an egg. In the second half, we activated the sperm but delayed the moment of fertilisation by 25 seconds and thus selected for the longer swimming sperm. In this treatment only sperm that were still swimming after this period of time (about 50%) were able to fertilise an egg.
We then reared the offspring to adulthood and measured number of offspring produced throughout life and measured lifespan. We found that sperm that were able to swim for longer sired offspring that not only produced more and healthier offspring but also lived for longer than their full siblings sired by sperm with reduced swimming ability. Our previous research (Alavioon et al. 2017 PNAS) suggests that these differences are caused at least partly by genetic differences among sperm. (more…)
Author Interviews, Genetic Research, OBGYNE / 18.02.2019
Ultrasensitive DNA Screening for Down Syndrome Offers Potential for Early Detection
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Zhiyong Zhang PhD
Key Laboratory for the Physics and Chemistry of Nanodevices
Department of Electronics
Peking University
Beijing China
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Down syndrome is caused by the presence of an extra 21st chromosome within the genome and is the most common birth defect (occurring in approximately 1 in 800 births). In the absence of a multiplexed quantitative diagnostic device, pregnant women have been examined with the ultrasound and the indirect biochemical markers (Alpha-fetoprotein, chorionic gonadotropin and free estriol) which are accompanied with a high misdiagnosis rate. And the diagnostic test (such as amniocentesis) following the wrong screening test results will bring harm to both the pregnant women and the fetuses.
Through PCR (polymerization chain reaction) amplification of the fetal DNA in the pregnant mother’s peripheral blood and fluorescence read-out, whole-genome sequencing (WGS)-based non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) sequences all the genomic DNA segments in parallel and quantitatively compares the percentage of different chromosomes, which increases the sensitivity for prenatal detection of Down syndrome. However, the complex instrumental setups and the resulted high processing cost present challenges for the large-scale application of WGS-based diagnosis at the point of care in the urban and rural areas of developing countries. Hence, beside the costly WGS method, there is an urgent need to develop a cost-effective NIPT biochip with simple instrumental setting, fast detection speed, high sensitivity, and programmable to multiple disease markers.
Taking advantages of we have developed a novel field effect transistor (FET) based biosensor that reveals a fast, ultra-sensitive, highly specific and cost-effective methods and someday can be used to detect fetal Down syndrome in NIPT. (more…)
Author Interviews, Exercise - Fitness, Geriatrics, Nutrition, Protein, Weight Research / 18.02.2019
Higher Protein, Lower Calorie Diet Can Improve Function and Weight Loss in Older Adults
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Kristen M. Beavers PhD, MPH, RD
Assistant Professor, Department of Health and Exercise Science
Department of Biostatistical Sciences
Wake Forest School of Medicine
Winston-Salem, NC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Weight loss recommendation for older adults with obesity is controversial, in part because overall weight loss is accompanied by loss of muscle and bone, which may exacerbate age-related risk of disability and fracture. Identification of interventions that can preserve muscle and bone while promoting fat loss should maximize cardiometabolic benefit, while minimizing potential harm to the musculoskeletal system.
This randomized controlled trial was originally designed to test whether a higher protein, nutritionally complete meal plan could preserve lean mass and mobility in older adults undergoing a six month intentional weight loss program. Four publications have resulted from this study: * “Effect of an Energy-Restricted, Nutritionally Complete, Higher Protein Meal Plan on Body Composition and Mobility in Older Adults with Obesity,” Journals of Gerontology: Medical Sciences, published online in advance of print June 21, 2018 * “Effect of a Hypocaloric, Nutritionally Complete, Higher-Protein Meal Plan on Bone Density and Quality in Older Adults With Obesity,” American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, published online in advance of print Jan. 9, 2019 * “Effect of Intentional Weight Loss on Mortality Biomarkers in Older Adults With Obesity,” Journals of Gerontology: Medical Sciences, published online in advance of print Aug. 20, 2018 * “Effects of a Hypocaloric, Nutritionally Complete, Higher Protein Meal Plan on Regional Body Fat and Cardiometabolic Biomarkers in Older Adults with Obesity,” Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, published online in advance of print Feb. 11, 2019
Across the four publications, we found that:
* Participants lost about 18 pounds, most of it fat (87 percent), and preserved muscle mass. The control group lost about half a pound.
* Even when participants lost weight, they maintained bone mass. In fact, trabecular bone score, a measure of bone quality which predicts fracture risk, seemed to improve.
* Fat was lost in the stomach, hips, thighs and rear, which is important for preventing or controlling cardiometabolic diseases such as diabetes and stroke.
* Participants’ score on the Healthy Aging Index, which measures biomarkers that predict mortality and longevity, improved by 0.75 points. (more…)
Author Interviews, Dermatology, Eli Lilly / 16.02.2019
Lilly Announces Phase 3 Results for Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lotus Mallbris, MD PhD
Dermatologist and Vice President, Head of Global Immunology Drug Development
Platform Team Leader at Lilly
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you briefly explain what is meant by atopic dermatitis? How common is this condition?
Response:The BREEZE-AD1 and BREEZE-AD2 clinical trials are multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baricitinib monotherapy in adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. These are two of five studies that will be part of the placebo-controlled data program intended to support global registrations.
Atopic dermatitis, a serious form of eczema, is a chronic, relapsing skin disease characterized by intense itching, dry skin and inflammation that can be present on any part of the body. It affects approximately 1-3 percent of adults worldwide.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Inflammation, JAMA, Kidney Disease, Pain Research, Stanford / 16.02.2019
Highest NSAID Usage Levels in Working Age Adults Linked to Greater Risk of Kidney Disease
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Alan Nelson, MPAS, PhD
Division of Primary Care and Population Health, Department of Medicine
Stanford University School of Medicine
Stanford, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The past research literature has provided relatively little information on the appropriate level of concern regarding non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and kidney disease risk among younger, apparently healthy patients. Clinicians are generally most concerned about the effects of these medications on the kidneys among patients with existing renal impairment and persons at risk for it, especially older patients.
Given that NSAID use appears to be high and rising in the US, we were interested in developing evidence on this topic in a population of working-age adults.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Heart Disease, Sleep Disorders / 16.02.2019
Sleep is Good For Your Health, Including Your Heart!
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Cameron S. McAlpine, Ph.D.
Banting Postdoctoral Fellow
Center for Systems Biology
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Boston, MA, 02114
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Cardiovascular disease is caused by the build up of white blood cells and fat in arteries. We have known for a long time that poor sleep is associated with an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. A number of human observational studies have found this correlation. However, the reasons for this correlation have been largely unknown.
Our study, performed in mice, provides one possible explanation. We found that when we disturbed the sleep of mice they produced more inflammatory white blood cells. These cells caused larger lesions in their arteries and more advanced cardiovascular disease.
We found that his phenomenon is controlled by a hormone produced in the brain that normally suppresses the production of white blood cells. When mice have their sleep disturbed this pathway breakdown causing the increased production of white blood cells.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Emory, JAMA, Prostate Cancer, Radiation Therapy / 15.02.2019
Hypofractionated Radiation for Low Risk Prostate Cancer Saves Time and Money
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Deborah Watkins Bruner RN, PhD, FAAN
Senior Vice President of Research
Emory University
Professor and Robert W. Woodruff Chair in Nursing
Nell Hodgson Woodruff School of Nursing
Professor, Department of Radiation Oncology
Emory University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: In a randomized clinical trial entitled, “Quality of Life in Patients With Low-Risk Prostate Cancer Treated With Hypofractionated vs Conventional Radiotherapy” the NRG Oncology Group previously demonstrated that men with low risk prostate cancer had similar 5-year disease- free survival of about 85% when treated with either conventional radiotherapy (C-RT) of 73.8 Gy in 41 fractions over 8.2 weeks, or with hypofractionated radiotherapy (H-RT) of 70 Gy in 28 fractions over 5.6 weeks. However, late physician reported side effects of mild bowel and bladder symptoms were increased in patients treated with H-RT and raised questions if the H-RT arm is acceptable to patients.
The current study asked the patient’s directly about their bowel, bladder, sexual function, anxiety, depression and general quality of life using valid patient reported questionnaires. These questionnaires have been found to be more accurate for reporting patient symptoms than physician report alone.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Dermatology, JAMA, Johns Hopkins, Microbiome / 15.02.2019
Antibiotics for Acne Alter Skin Microbiome
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Luis Garza, MD-PhD
Associate Professor
Department of Dermatology
Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
Baltimore, MD 21287
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings? Do you think these findings would be similar with other antibiotics (oral or topical) or with isotretinoin for acne?
Response: We prescribe antibiotics frequently for acne. We certainly know it affects our normal and abnormal bacteria on our skin. But we don’t fully understand how well or not people recover from antibiotics.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Heart Disease, JAMA, Surgical Research / 15.02.2019
Aortic Stenosis Staging Helps Predict TAVR Outcomes
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
JOÃO L. CAVALCANTE, MD, FASE, FACC, FSCCT, FSCMR
Director, Cardiac MRI and Structural CT Labs
Director, Cardiovascular Imaging Research Core Lab
Minneapolis Heart Institute
Abbott Northwestern Hospital
Minneapolis, MN, 55407
MIHO FUKUI MD
Division of Cardiovascular Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Heart & Vascular Institute, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Minneapolis Heart Institute, Abbott Northwestern Hospital, Minneapolis, Minnesota
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Recent study by Généreux et al (1), using the Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valves (PARTNER) 2A and 2B data, provided the first framework of a staging system for severe aortic stenosis (AS) that quantifies the extent of structural and functional cardiac change associated with AS and importantly its association with 1-year mortality in patients receiving either surgical or transcatheter AVR (TAVR):
- Stage 0: No other cardiac damage;
- Stage 1: LV damage as defined by presence of LV hypertrophy, severe LV diastolic, or LV systolic dysfunction;
- Stage 2: Left atrium or mitral valve damage or dysfunction;
- Stage 3: Pulmonary artery vasculature or tricuspid valve damage or dysfunction; and
- Stage 4: right ventricular damage.
ALS, Author Interviews, Statins / 15.02.2019
Could Statins Protect Against ALS?
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Alastair J. Noyce MD, PhD
Preventive Neurology Unit,
Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine
Queen Mary University of London,
Department of Clinical and Movement Neurosciences,
University College London, Institute of Neurology,
London UK
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or motor neurone disease (MND) is a relentlessly progressive disorder that affects nerves which supply muscles. Over time the nerves die, leading to limb weakness, speech and swallowing problems, and ultimately breathing problems. Patients die on average 3-5 after diagnosis. There is no cure and the underlying disease processes are only understood in part.
In this study, we adopted a large-scale approach to exploring causal risk factors for ALS. Causality is important because it implies that if one could modify or induce a change in a risk factor, one would observe a change in the risk of ALS. Observational studies struggle to prove causality definitely. Associations in observational studies can arise because:
1) the risk factor truly changes risk of ALS; or
2) something about ALS changes one’s exposure to the risk factor; or
3) the presence of another factor, which may or may not be known, can induce an association between a risk factor and ALS. Unless scenario 1 represents the truth, then changing the risk factor will not have any effect on risk of ALS.
We used a proxy-based approach, known as Mendelian randomisation, to assess hundreds of possible risk factors for ALS for evidence of causality. What emerged from this was a very clear signal linking LDL cholesterol to risk of ALS. (more…)
Author Interviews, Cancer Research, Hepatitis - Liver Disease, Lancet / 14.02.2019
Hepatitis C: Study finds Direct Acting Antivirals Reduce Mortality and Liver Cancer
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: [caption id="attachment_47495" align="alignleft" width="133"] Prof. Carrat,[/caption] Prof. Fabrice Carrat, MD, PhD Institut Pierre Louis d'Épidémiologie et de Santé Publique, Paris, France MedicalResearch.com:...
Author Interviews, Heart Disease, JACC / 13.02.2019
Multiple Modifiable Risk Factors in Young Adults with Heart Attack
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Srikanth Yandrapalli, MD
Chief Resident in Internal Medicine at New York Medical College at
Westchester Medical Center Program
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Risk factors play an important role in the development of and progression of coronary heart disease, thus necessitating strategies to address the leading modifiable risk factors to reduce the burden of coronary heart disease. Data are lacking regarding therecent temporal trends in the prevalence of these risk factors during a first AMI in US young adults.
In our study, we report that among young adults in the US with a first acute myocardial infarction, the prevalence rates of major modifiable risk factors were very high with over 90% of patients having at least 1 such risk factor. Significant sex and racial disparities were observed. Sex differences in the rates of certain risk factors were clearly evident with males having higher rates of smoking, dyslipidemia, and drug abuse, whereas females had higher rates metabolic risk factors like diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and obesity. Sex differences in the rates of certain risk factors narrowed with increasing age and over time. Blacks had higher rates of hypertension, obesity, and drug abuse, Whites had higher rates of smoking, Hispanics had higher rates of diabetes mellitus and patients of Asian/Pacific Islander race had higher rates of dyslipidemia. Prevalence rates progressively increased between 2005 and 2015 except for dyslipidemia for which a decreasing trend was noted more recently. (more…)
Author Interviews, BMJ, Cancer Research, HPV, OBGYNE / 13.02.2019
HPV Testing for Primary Cervical Cancer Screening
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Matejka Rebolj, PhD
King’s College London, London, UK
Professor Henry Kitchener, MD FRCOG FRCS
University of Manchester, Manchester, UK
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We now have reliable and affordable technologies to detect human papillomavirus (HPV), a virus which is universally accepted as the cause of cervical cancer. Various large trials confirmed that cervical screening could be improved by replacing the smear (cytology) test that has been in use for decades, with HPV testing. Many countries are now making the switch. In England, this is planned for the end of 2019. To test how to run HPV testing within the English National Health Service, a pilot was initiated in 2013 in six screening laboratories. We also wanted to determine whether the encouraging findings from the trials could be translated to everyday practice. This is important not only because we will be using different HPV tests, but also because women undergoing screening in trials are much more selected than those who are invited to population-based screening. (more…)
Annals Internal Medicine, Author Interviews, Exercise - Fitness, Heart Disease, Karolinski Institute, Weight Research / 13.02.2019
Poor Fitness and Obesity in Early Life Linked to Greater Disability as Adult
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Pontus Henriksson | PhD and Registered Dietitian
Postdoctoral Researcher | SFO-V Fellow
Department of Biosciences and Nutrition
Karolinska Institutet
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: In many countries, disability pensions are granted to working-aged persons who are likely to never work full-time again because of a chronic disease or injury diagnosed by a physician. In addition to serving as an important indicator of chronic disease, disability pensions are associated with high societal costs.
Hence, we examined whether cardiorespiratory fitness and obesity (two potentially modifiable factors) were associated with disability pension later in life.
Our main findings were that low physical fitness and/or obesity during adolescence, were strongly associated with disability pension later in life due to a wide range of diseases and causes. (more…)
Author Interviews, Beth Israel Deaconess, Blood Pressure - Hypertension, Salt-Sodium / 13.02.2019
Does Salt Help or Worsen Lightheadedness?
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Stephen P. Juraschek, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor, Harvard Medical School
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Division of General Medicine, Section for Research
Boston, MA 02215
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Lightheadedness with standing is an important risk factor for falls. Sodium is often considered a treatment for lightheadedness with standing.
We examined this in the setting of a monitored feeding study where adults ate each of 3 different sodium levels for 4 weeks at a time. Participants took 5 day breaks between sodium levels and ate the sodium levels in random order. We tested the hypothesis that lowering sodium would worsen how much lightheadedness the study participants reported.
(more…)
Author Interviews, JAMA, Prostate Cancer, Radiation Therapy / 12.02.2019
Stereotactic Radiation Can Condense Treatment Times For Prostate Cancer
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Amar U. Kishan, MD
Assistant Professor
Department of Radiation Oncology
University of California, Los Angeles
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Typical external beam radiation courses range up to 8-9 weeks in length (39-45 treatments). There are data that shorter courses, delivering a higher dose per day, may be just as effective.
Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) really pushes this concept by condensing the treatment to just four to five treatments, with a high dose per day.
Here, we present the pooled results of the outcomes of 2142 men with low and intermediate risk prostate cancer and a median of 6.9 years of followup.
We demonstrate a very favorable efficacy and safety profile. Specifically, the rates of recurrences were 4.5% and 10.2% for low and intermediate risk disease at 7 years, and rates of late severe toxicity were 2.4% for urinary toxicity and 0.4% for gastrointestinal toxicity.
(more…)
Author Interviews, MRI, Prostate Cancer, Technology / 12.02.2019
Radiomics Plus Machine Learning Can Optimize Prostate Cancer Classification
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Gaurav Pandey, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor
Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences
Icahn Institute of Data Science and Genomic Technology
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) has become increasingly important for the clinical assessment of prostate cancer (PCa), most routinely through PI-RADS v2, but its interpretation is generally variable due to its relatively subjective nature.
Radiomics, a methodology that can analyze a large number of features of images that are difficult to study solely by visual assessment, combined with machine learning methods have shown potential for improving the accuracy and objectivity of mpMRI-based prostate cancer assessment. However, previous studies in this direction are generally limited to a small number of classification methods, evaluation using the AUC score only, and a non-rigorous assessment of all possible combinations of radiomics and machine learning methods. (more…)
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Keith Schneider PhD
Director, Center for Biomedical and Brain Imaging
Associate Professor
Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences
University of Delaware
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Absolute pitch is the ability to name a musical note in isolation. It is rare in the population, approximately 1/10,000 people have it. The neural mechanisms of this ability have not been clear. It is not known whether people with absolute pitch encode auditory frequencies differently, or whether absolute pitch derives from the same sensory encoding but different memory connections.
We tested 20 people with absolute pitch, 20 matched musicians with the same number of years of musical training, age of onset of musical training, and number of hours of practice per week, as well as 20 controls with minimal musical training.
The main findings are that people with absolute pitch have larger early auditory cortex—primary auditory cortex was enlarged about 50% relative to the other two groups, which did not differ significantly from each other. We also found that the tuning bandwidth of the individual voxels in the early auditory cortical areas was broader in people with absolute pitch.
That is, these small bits of the brain responded to a wide range of frequencies than those in the other two groups. This suggested to us that people with absolute pitch might imply what is known as “ensemble encoding”. That is, they use a larger network of neurons to encode sounds. (more…)
Author Interviews, CDC, JAMA, Opiods / 12.02.2019
Most Counties See Opioid Prescription Rates Falling
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Gery Guy, PhD, MPH
Injury Center
CDC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: This study examined opioid prescribing at the national and county-level in 2015 and 2017.
During 2015 to 2017, the amount of opioids prescribed decreased 20.1% in the United States. The amount of opioids prescribed per person varies substantially at the county-level. The average amount of opioids prescribed in the highest quartile of counties was nearly 6 times the amount in the lowest quartile. Reductions in opioid prescribing could be related to policies and strategies aimed at reducing inappropriate prescribing, increased awareness of the risks associated with opioids, and release of the CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Cancer Research, Prostate Cancer, Radiation Therapy / 12.02.2019
Veyonda Enhanced Benefit of Radiation Therapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Trial
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Graham Kelly, BSc (Vet) (Hons, BVSc (Hons), PhD
Managing Director and Chief Executive Officer
Noxopharm
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this announcement? What are the main findings?
Response: Veyonda is an experimental drug being developed as a means of enhancing the anti-cancer effect of radiotherapy. The Phase 1b DARRT-1 study is assessing the ability of Veyonda to boost a palliative dose of external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) applied to a single lesion, to result in a systemic response in non-irradiated lesions (known as an abscopal response) in men with metastatic, end-stage prostate cancer. The aim is to provide at the least better palliation, and at best a survival advantage. The reported data concerns the study’s initial dose-finding arm involving three different dosages of Veyonda. This arm involves 12 subjects and the report concerns their clinical status at 12-weeks post-irradiation. The data provide clinical evidence of an abscopal effect in at least half of the eight subjects receiving the two highest Veyonda dosages and demonstrate that the combination of Veyonda and palliative radiotherapy was well-tolerated. The 1200 mg dosage was confirmed as the therapeutic dose.
(more…)
Aging, Author Interviews, Genetic Research / 12.02.2019
12 Genetic Loci Associated with Human Healthspan
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Yurii Aulchenko Co-founder and Chief Scientist of PolyOmica
PolyOmica is a research & development company providing services and tools for quantitative genetics and functional genomics.
Peter Fedichev Founder and Chief Science Officer of Gero
Gero is a data-driven longevity company developing innovative therapies that will strongly extend the healthy period of life also known as healthspan
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Peter Fedichev, Gero: Age is the most important risk factor behind age-related diseases and death. Lifespan has increased quite dramatically over the last 150-200 years mostly due to the eradication of early-life mortality. What we find, however, is that the healthspan, understood as the chronic diseases-free period, is also on the rise, but not so much. It appears that lifespan is modifiable by interventions, at least in lab animals. It is therefore crucial to understand if the biology behind human healthspan. Is it the same as that of lifespan? What are the molecular pathways and genetic factors controlling the healthspan? At the end, we would like to develop interventions that extend not only lifespan, but also the healthspan. Everyone wants to stay healthy!
Yurii Aulchenko, PolyOmica: We studied the incidence of the most prevalent age-related diseases in the large UK Biobank, one of the best repositories of biologically and medically relevant data from a very large cohort of aging individuals. We observed that the incidence (the chances of) all the major diseases increased exponentially with age. The diseases risk doubling time was about eight years, same as the mortality doubling time from the Gompertz mortality law, discovered as early as in 1825 and used in life insurance ever since. The similar patterns of age-dependent risk acceleration suggest a major common driver behind the diseases, that is most plausibly aging itself.
Peter Fedichev, Gero: The incidence of the diseases could, therefore, be used as a biomarker of aging process. We used the age at the onset of the first age-related disease (the end of healthspan) as the target for a genome-wide association study (GWAS) and identified as many as 12 genetic loci associated with human healthspan. (more…)
Author Interviews, Genetic Research, JAMA, Race/Ethnic Diversity, Stroke / 11.02.2019
Link Between Apolipoprotein E and Brain Hemorrhage Varies by Ethnicity
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Sandro Marini, MD
Research Fellow
Jonathan Rosand Laboratory
Massachusetts General Hospital
Boston, MA 02114
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The epsilon(ε) 4 allele of the Apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene increases risk for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH).
In both diseases, it is believed to increase risk through the deposition of beta-amyloid within the brain and blood vessels, respectively. The effect of APOE ε4 on both AD and ICH risk changes across populations, for unclear reasons.
In our study, we confirmed the role of APOE ε4 for ICH risk in whites and found that the risk-increasing effect of the 4 allele is demonstrable in Hispanics only when balancing out the effect of hypertension.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Dermatology, JAMA, Kidney Disease, Melanoma, Transplantation / 11.02.2019
Kidney Transplant Patients at Increased Risk of Skin Cancer, Even After Graft Stops Working
MedicalResearch.com Interview with
 Donal J. Sexton, MD, PhD
Department of Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation
Beaumont Hospital
Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
Dublin, Ireland
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Patients who receive a kidney transplant as treatment for end stage kidney disease are at risk of malignancy due to immunosuppression. In contrast to
other solid organ transplant types, when kidney transplants fail it is possible for recipients to return to dialysis. Immunosuppression is usually reduced or completely stopped when the allograft fails due to the risk of infection on dialysis.
We decided to investigate what the trajectory of risk for non-melanoma skin cancer and invasive cancers overall (composite group) looked like for patients who have received multiple consecutive kidney transplants with intervening periods of graft failure. We compared cancer risk during periods of allograft failure and periods of functioning kidney transplants. (more…)
Donal J. Sexton, MD, PhD
Department of Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation
Beaumont Hospital
Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
Dublin, Ireland
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Patients who receive a kidney transplant as treatment for end stage kidney disease are at risk of malignancy due to immunosuppression. In contrast to
other solid organ transplant types, when kidney transplants fail it is possible for recipients to return to dialysis. Immunosuppression is usually reduced or completely stopped when the allograft fails due to the risk of infection on dialysis.
We decided to investigate what the trajectory of risk for non-melanoma skin cancer and invasive cancers overall (composite group) looked like for patients who have received multiple consecutive kidney transplants with intervening periods of graft failure. We compared cancer risk during periods of allograft failure and periods of functioning kidney transplants. (more…)
 Donal J. Sexton, MD, PhD
Department of Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation
Beaumont Hospital
Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
Dublin, Ireland
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Patients who receive a kidney transplant as treatment for end stage kidney disease are at risk of malignancy due to immunosuppression. In contrast to
other solid organ transplant types, when kidney transplants fail it is possible for recipients to return to dialysis. Immunosuppression is usually reduced or completely stopped when the allograft fails due to the risk of infection on dialysis.
We decided to investigate what the trajectory of risk for non-melanoma skin cancer and invasive cancers overall (composite group) looked like for patients who have received multiple consecutive kidney transplants with intervening periods of graft failure. We compared cancer risk during periods of allograft failure and periods of functioning kidney transplants. (more…)
Donal J. Sexton, MD, PhD
Department of Nephrology and Kidney Transplantation
Beaumont Hospital
Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland
Dublin, Ireland
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Patients who receive a kidney transplant as treatment for end stage kidney disease are at risk of malignancy due to immunosuppression. In contrast to
other solid organ transplant types, when kidney transplants fail it is possible for recipients to return to dialysis. Immunosuppression is usually reduced or completely stopped when the allograft fails due to the risk of infection on dialysis.
We decided to investigate what the trajectory of risk for non-melanoma skin cancer and invasive cancers overall (composite group) looked like for patients who have received multiple consecutive kidney transplants with intervening periods of graft failure. We compared cancer risk during periods of allograft failure and periods of functioning kidney transplants. (more…)
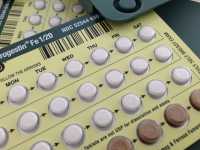
Author Interviews, Gender Differences, OBGYNE, Psychological Science, Sexual Health / 11.02.2019
Birth Control Pills May Make It Harder for Women To Identify Complex Emotions
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Alexander Lischke, Dipl.-Psych.
Universität Greifswald
Institut für Psychologie
Physiologische und Klinische Psychologie/Psychotherapie
University of Greifswald, Germany
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We know for a long time that cyclic variations in womens' estrogen and progesterone levels affect their emotion recognition abilities by modulating neural activity in brain regions implicated in emotion processing. We also know that oral contraceptives suppress cyclic variations in womens' estrogen and progesterone levels. We, thus, assumed that oral contraceptives would affect womens' emotion recognition abilities due to the aforementioned suppression of cylic variations in estrogen and progesterone levels that modulate neural activity in brain regions during emotion processing. To test this assumption, at least with respect to the behavioral effects of oral contraceptive use on emotion recognition, we performed the current study.
We recruited regular cylcling women with and without oral contraceptive use for our study. None of the women were in psychotherapeutical or psychopharmacological treatment at the time of the study. During the study, women performed a emotion recognition task that required the recognition of complex emotional expressions like, for example, pride or contempt.
(more…)