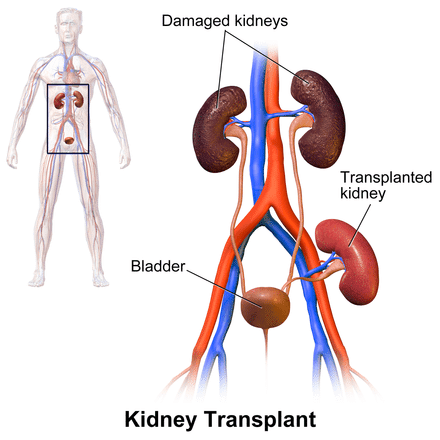
Author Interviews, Inflammation, Kidney Disease, Nature, Rheumatology / 08.02.2024
Lupus: Monash Scientists Developing Modified Immune Cells to Protect Patients from Kidney Disease
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
A/Prof. Joshua Ooi, PhD
Head, Regulatory T-cell Therapies
Translational Research Facility
Clinical Sciences at Monash Health,
Monash University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: In 2017, we published a landmark Nature paper showing that people who are protected from autoimmune disease have specialized molecules on immune cells. These specific molecules are missing in patients that develop autoimmune disease.
(more…)





 Wilson N. Merrell
Ph.D. Student
Wilson N. Merrell
Ph.D. Student


 Lauren C. Davis, MBS
Department of Medical Education
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Scranton, PA 19409
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Financial conflicts of interest (COIs) resulting from ties between academia and industry have been under scrutiny for their potential to hinder the integrity of medical research. COIs can lead to implicit bias, compromise the research process, and erode public trust (1-6). The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), standardizes symptom criteria and codifies psychiatric disorders. This manual contributes to the approval of new drugs, extensions of patent exclusivity, and can influence payers and mental health professionals seeking third-party reimbursements. Given the implications of the DSM on public health, it is paramount that it is free of industry influence. Previous research has shown a high prevalence of industry ties among panel and task force members of the DSM-IV-TR and DSM-5, despite the implementation of a disclosure policy for the DSM-5 (7,8). This study (9) determined the extent and type of COIs received by panel and task-force members of the DSM-5-TR (2022) (10). As the DSM-5-TR did not disclose COI, we used the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services Open Payments (OP) database (11) to quantify them.
Lauren C. Davis, MBS
Department of Medical Education
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Scranton, PA 19409
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Financial conflicts of interest (COIs) resulting from ties between academia and industry have been under scrutiny for their potential to hinder the integrity of medical research. COIs can lead to implicit bias, compromise the research process, and erode public trust (1-6). The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), standardizes symptom criteria and codifies psychiatric disorders. This manual contributes to the approval of new drugs, extensions of patent exclusivity, and can influence payers and mental health professionals seeking third-party reimbursements. Given the implications of the DSM on public health, it is paramount that it is free of industry influence. Previous research has shown a high prevalence of industry ties among panel and task force members of the DSM-IV-TR and DSM-5, despite the implementation of a disclosure policy for the DSM-5 (7,8). This study (9) determined the extent and type of COIs received by panel and task-force members of the DSM-5-TR (2022) (10). As the DSM-5-TR did not disclose COI, we used the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services Open Payments (OP) database (11) to quantify them.











 Lisa-Marie Smale, PharmD
Lisa-Marie Smale, PharmD