Updated Classification of Acute MI Based on Stages of Tissue Injury Severity
Crohn’s Disease: Lilly’s Mirikizumab Has Potential to Achieve Remission in Phase 3 Study
Ulcerative Colitis: FDA Approves Mirikizumab After Study Finds Long Lasting Response
Healthy Eating: Top 5 Best Diets to Follow
 US News & World Report announced that the Mediterranean style of eating is the best overall diet for 2023. Only 24 diets were ranked instead of 40 that were analyzed in the past years. Vegan, vegetarian, Nordic, traditional Asian and the glycemic index were integrated into the Mediterranean because of the ‘underlying plant-based principles.’ According to managing editor Gretel Schueller who oversees the annual diet ranking, they are always looking for more health conditions that they can address, but the lack of scientific data for examining other types of diets is a constraint.
US News & World Report announced that the Mediterranean style of eating is the best overall diet for 2023. Only 24 diets were ranked instead of 40 that were analyzed in the past years. Vegan, vegetarian, Nordic, traditional Asian and the glycemic index were integrated into the Mediterranean because of the ‘underlying plant-based principles.’ According to managing editor Gretel Schueller who oversees the annual diet ranking, they are always looking for more health conditions that they can address, but the lack of scientific data for examining other types of diets is a constraint.Face-to-Face: Study Finds Peak Viral Transmission Occurs Within 5 Seconds
Study Finds Enhanced Tai Ji Quan Practice Improved Memory and Walking in Older Adults
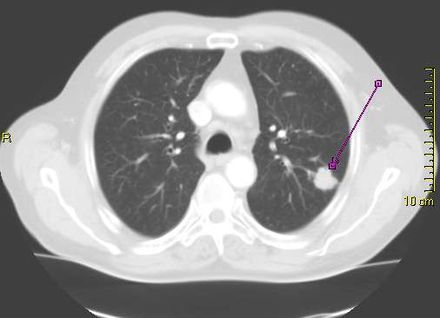
Lung Cancer: Stanford Risk-Based Model Reduces Screening Disparities
- Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States, killing about 127,000 people annually, but it can be treatable if detected early.
- Low-dose computed tomography, or CT scan, has been shown to significantly reduce the number of lung cancer deaths. But because the radiation delivered by the scans can be harmful (they use on average about 10 times the radiation of standard X-rays), only those people at relatively high risk for lung cancer should be screened. The two biggest risk factors for lung cancer are exposure to tobacco smoke and age. Current national guidelines that rely on age and smoking exposure to recommend people for lung cancer screening are disproportionally failing minority populations including African Americans, according to a new study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine.
- In 2021, the national guidelines by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) issued revised recommendation guidelines on lung cancer screening, lowering the start age from 55-year to 50-year and the smoking pack-year criterion from 30 to 20, compared to the 2013 USPSTF criteria. In comparison to the 2013 criteria, the new modifications have been shown to lessen racial disparities in screening eligibility between African Americans and Whites. However, potential disparities across other major racial groups in the U.S., such as Latinos, remains poorly examined.
- Meanwhile, risk prediction model assesses a person’s risk score of developing an illness, such as lung cancer.
CDC Reports Outcomes of Pediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome After COVID
Monash Study Highlights Association Between Triglycerides and Risk of Dementia
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: [caption id="attachment_60963" align="alignleft" width="133"] Dr. Zhen Zhou[/caption] Zhen Zhou, PhD Research Fellow, Chronic Disease & Ageing Monash University MedicalResearch.com: What is the background...
Mt. Sinai Study Finds PFAS Chemicals May Be Associated with Increased Risk of Thyroid Cancer
Baylor College of Medicine Scientists Find Potential Link Between Common Fungus and Alzheimer’s
ObesityWeek23: Study Suggests Persons with Obesity at Greatest Risk are Receiving Medications They Need
Emory/CDC Study Finds Combination Strategy Reduces Hospital Acquired Staph Infections
Long-Term Stable Wearable Patch Can Measure Important Biomarkers in Sweat
(more…)
Study Identifies Genes Linked to Nodular Melanoma
Outcomes of Prophylactic Salpingo-Oophorectomy After BRCA1/2 Breast Cancer Resection
UCLA Animal Study Finds It is Becoming Possible To Partially Restore Walking By Stimulating Nerve Fibers
Low Income and Minority Children Risk Impaired Cognitive Function from Environmental Hazards
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Devon Payne-Sturges, DrPH, MPH, MEngr
Associate Professor
Maryland Institute for Applied Environmental Health
School of Public Health
University of Maryland, College Park
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: My co-authors and I conducted this study to fill a knowledge gap and to inform the work of Project TENDR. No systematic or scoping review had examined both exposure disparities and the joint effects of combined exposures of environmental neurotoxicants and social disadvantage as they relate to disparities in neurodevelopmental outcomes specifically among children living in the U.S.
Our study is the first to summarize the evidence on 7 neurotoxicants that children in the U.S. are routinely exposed to and we examined both disparities in these exposures and disparities in the effects of those exposures on children’s brain development, cognition, and behavior by race, ethnicity, and economic status.
We reviewed over 200 independent studies spanning five decades from 1974 to 2022 on social disparities in exposure to 7 exemplar neurotoxic chemicals and pollutants, including chemical mixtures, and their relationship with disparities with neurodevelopmental outcomes among children in the U.S.
USPSTF: Blood Pressure Should Be Monitored Throughout Pregnancy
 Esa M. Davis, M.D., M.P.H , F.A.A.F.P
Professor of Medicine and Family and Community Medicine
Associate Vice President of Community Health and
Senior Associate Dean of pPopulation Health and Community Medicine
University of Maryland School of Medicine
Dr. Davis joined the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in January 2021
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, including gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia, are among the leading causes of serious complications and death for pregnant people in the United States.
Pregnant women and pregnant people of all genders should have their blood pressure measured at each prenatal visit to help find and prevent serious health issues related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. (more…)
Esa M. Davis, M.D., M.P.H , F.A.A.F.P
Professor of Medicine and Family and Community Medicine
Associate Vice President of Community Health and
Senior Associate Dean of pPopulation Health and Community Medicine
University of Maryland School of Medicine
Dr. Davis joined the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force in January 2021
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, including gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia, are among the leading causes of serious complications and death for pregnant people in the United States.
Pregnant women and pregnant people of all genders should have their blood pressure measured at each prenatal visit to help find and prevent serious health issues related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. (more…)Emergency Room Study Finds ChatGPT Able to Think Much Like a Human Doctor
Study Finds Children of Addicted Parents Have Risk of Intellectual Disability
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Lotfi Khemiri
Centre for Psychiatry Research
Stockholm, Sweden
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Our study used large-scale national register data in close to 2 million children, and found that parental abuse of both alcohol and drugs are associated with increased risk of intellectual disability in the offspring. Importantly, the risk increase was observed in both mothers and fathers which to the best of our knowledge is a novel finding, and may be explained by both genetic and environmental factors including toxic effects of substance intake on fetal development.
(more…)
Lotfi Khemiri
Centre for Psychiatry Research
Stockholm, Sweden
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Our study used large-scale national register data in close to 2 million children, and found that parental abuse of both alcohol and drugs are associated with increased risk of intellectual disability in the offspring. Importantly, the risk increase was observed in both mothers and fathers which to the best of our knowledge is a novel finding, and may be explained by both genetic and environmental factors including toxic effects of substance intake on fetal development.
(more…)
Birthweight, Gestational Age and Later Cognitive Performance
USPSTF: PrEP Helps Prevent HIV but Not Other STDs. Safe Sex Still Important
No Observed Increase in Prescription Stimulant Use After Legalization of Medical Marijuana
Surgery: Post-Op Outcomes Differ by Gender of Surgeon
- We have been studying how the primary treating surgeons sociocultural characteristics impact the recovery of patients they are looking after.
- Specifically, we have been studying the effect of surgeon sex on outcomes such as death, complications and readmission after common and complex surgeries. These are outcomes that are important to patients and the health system.
- Previously, we showed that patients with a female surgeon had better short term (30 day) outcomes than similar patients having surgery with a man. This study asked the question of whether the sex of a patient’s surgeon affects patients’ longer term outcomes at 90 days and 1 year, after surgery.
Psoriasis: Case Study Finds Weight Loss Drug Semaglutide Reduced Fat Around Heart
Hemodialysis: Canadian Study Describes Improved Membrane to Reduce Complications
Associate Professor, Chemical and Biomedical Engineering
Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering
Division of Biomedical Engineering
University of Saskatchewan MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: The background of this study lies in the pursuit of improving the compatibility of dialysis membranes used in hospitals. My team sought to enhance the performance of these membranes by incorporating heparin, a widely recognized anticoagulant. Existing heparin-grafted membranes carried a negative charge, resulting in adverse blood-membrane interactions and complications for dialysis patients. The study aimed to overcome these issues and create a neutralized membrane surface that maintains the benefits of heparin while minimizing undesirable interactions. (more…)